How Does Weever Software Streamline Planned Cleaning in Food Production?
Streamline sanitation in food production with Weever. Automate cleaning schedules, track performance, and ensure compliance with real-time insights.
In the food production and related industries, maintaining cleanliness is a non-negotiable priority. Effective sanitation ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, safeguards product quality, and upholds consumer trust. However, managing the planned cleaning of food manufacturing processes can be a complex challenge, involving multiple areas, equipment, and personnel. Traditional methods of tracking and scheduling cleaning activities often lead to inefficiencies, missed tasks, and inconsistent execution, making it harder to sustain high standards. Weever software transforms this landscape by providing a streamlined, technology-driven approach to managing sanitation. By integrating a robust master sanitation schedule (MSS) into its platform, Weever simplifies planning, execution, and monitoring of cleaning activities in food production facilities. This blog explores how Weever software supports manufacturers in structuring and monitoring their master sanitation program, driving efficiency and ensuring compliance in every aspect of their operations.
Simplifying Sanitation Management with an Intuitive Interface
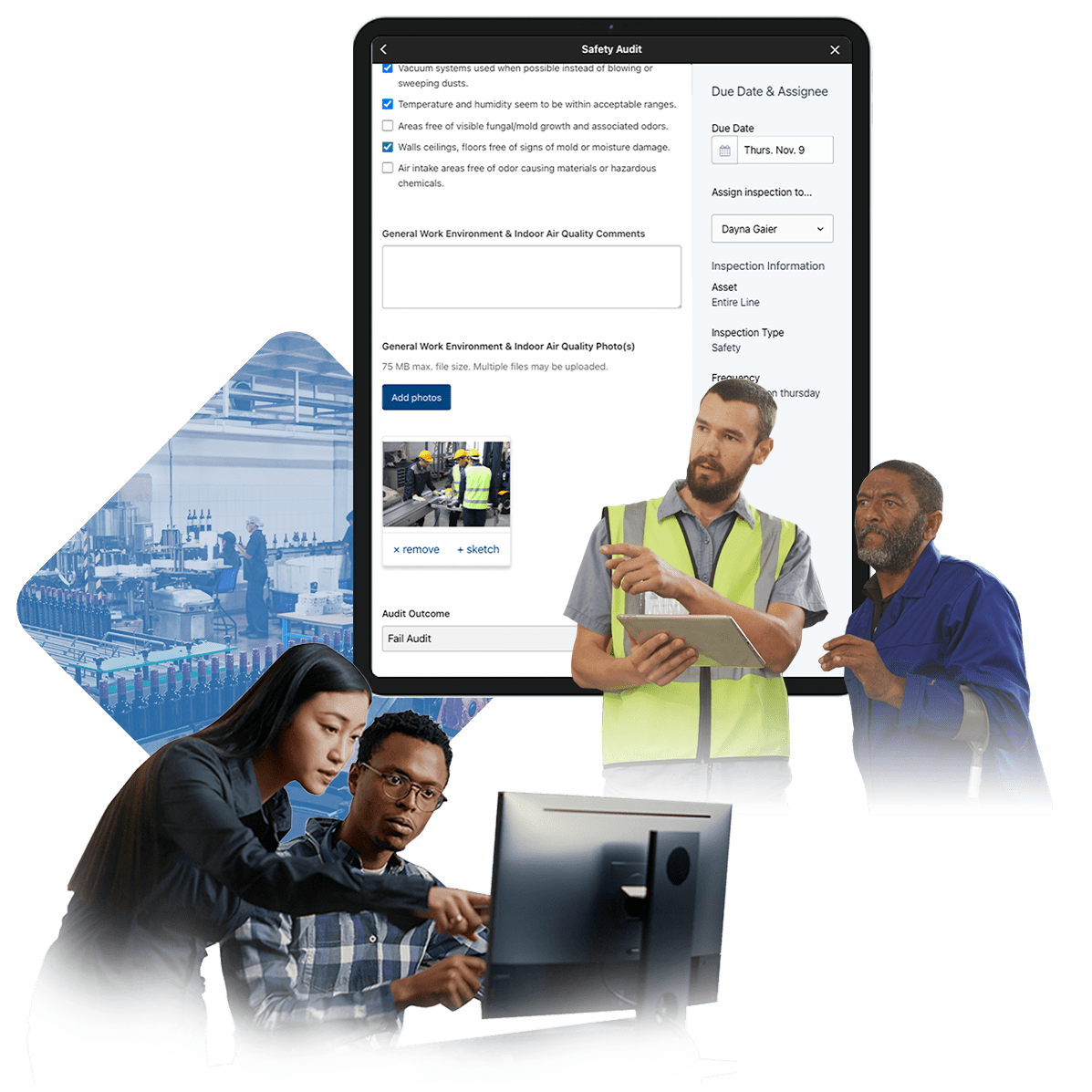
One of the most common challenges in managing a master sanitation schedule food manufacturing process is its inherent complexity. Assigning tasks, setting frequencies, and ensuring clarity across teams can be a daunting undertaking. Weever software addresses this issue by offering an intuitive interface designed specifically for the needs of food production facilities. With Weever, manufacturers can easily define the frequency of cleaning and sanitizing activities for different areas and equipment in the plant. The platform allows users to configure cleaning schedules based on their specific requirements, whether it's a high-contact surface that requires daily cleaning or equipment that needs periodic deep cleaning. Each activity can be labeled and organized logically, ensuring that teams have a clear understanding of what needs to be done and when. This user-friendly design reduces confusion, minimizes errors, and promotes seamless collaboration between operators, supervisors, and quality control staff.
Automating Workflows for Consistency and Efficiency
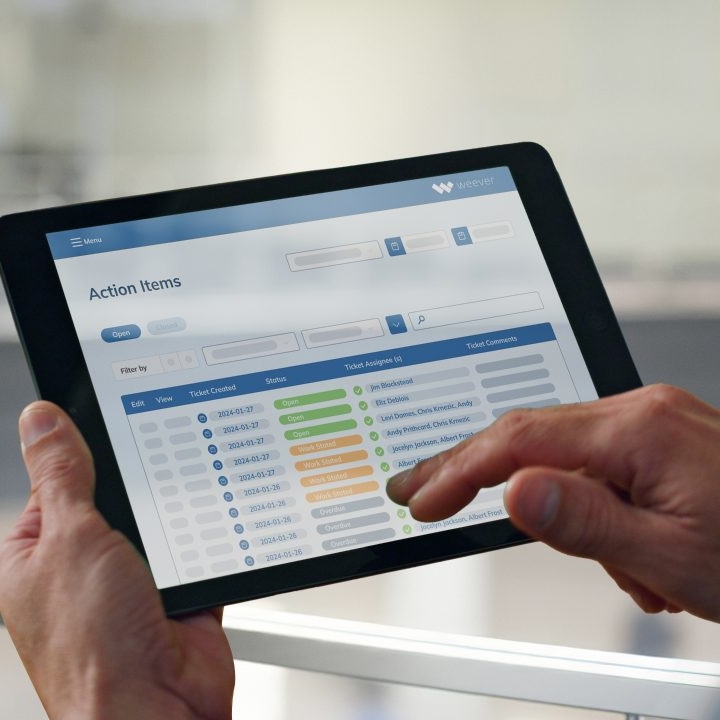
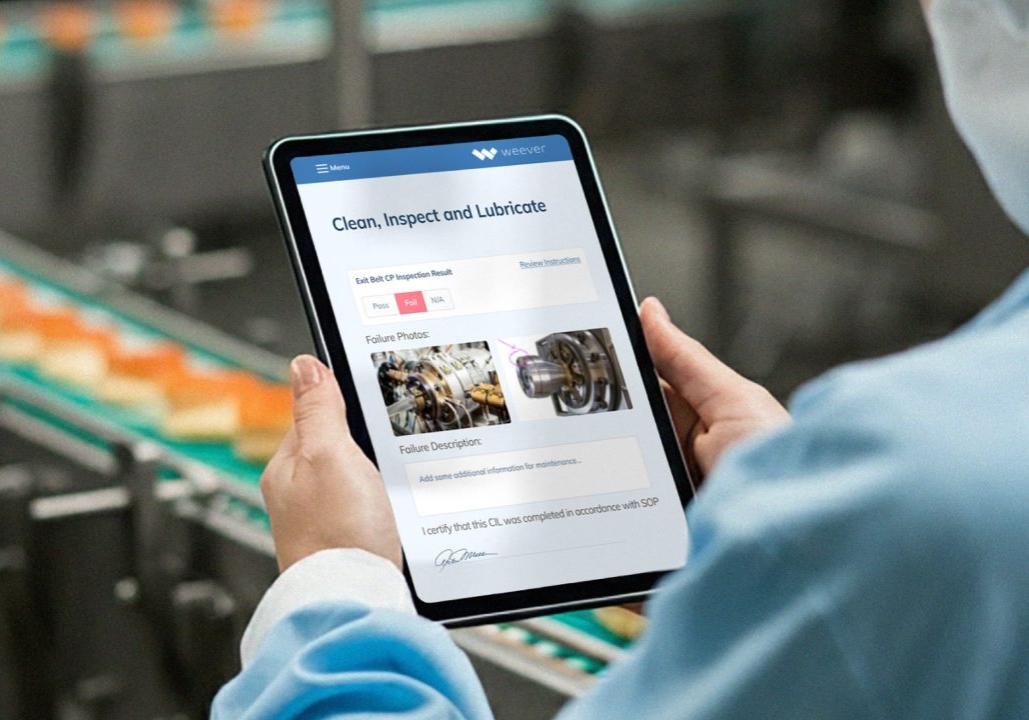
In food production, consistency is critical, particularly when it comes to cleaning and sanitation. A missed cleaning task or delayed schedule can compromise food safety and lead to regulatory penalties. Weever software ensures consistency through automated workflows that make managing the planned cleaning of food manufacturing activities effortless. The software automates the assignment of tasks, scheduling activities in advance and sending timely reminders to the relevant personnel. This ensures that no task is overlooked and that cleaning routines are performed on time. For example, a food plant master sanitation schedule can include specific instructions for cleaning production lines, storage areas, and other critical zones. Weever tracks these schedules in real time, ensuring that tasks are logged, monitored, and completed without manual intervention. Additionally, the platform enables supervisors to assign action items for any deviations discovered during cleaning. If an inspection reveals a cleanliness issue or equipment abnormality, Weever generates a corrective action plan and assigns it to the appropriate team members, ensuring swift resolution.
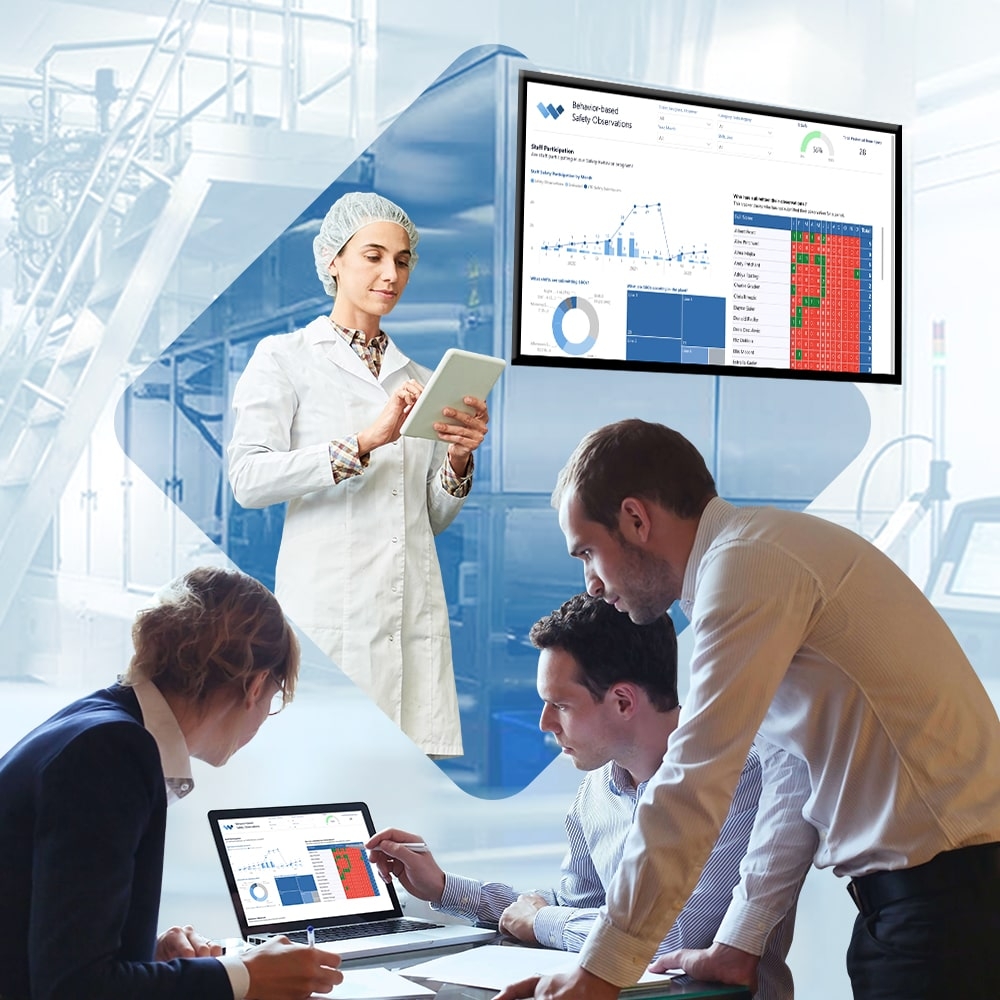
Leveraging Insights and Real-Time Reporting for Continuous Improvement
Effective sanitation management isn't just about completing tasks-it's also about improving processes over time. Weever software provides manufacturers with powerful insights into the performance of their master sanitation program, allowing them to identify opportunities for optimization. By analyzing cleaning activity data, Weever uncovers trends and patterns that can help manufacturers refine their processes. For instance, the platform might reveal that certain equipment requires more frequent cleaning due to high usage or that specific areas are consistently prone to delays. Armed with these insights, manufacturers can make informed decisions about adjusting their MSS cleaning in food safety practices to better align with operational needs. Real-time reporting is another critical feature of Weever software, providing instant visibility into the status of cleaning activities. Supervisors can monitor progress in real time, identifying incomplete or delayed tasks and addressing them proactively. This transparency not only ensures compliance with cleaning schedules but also builds a culture of accountability and attention to detail within the organization.
Ensuring Seamless and Structured Integration for Food Manufacturers
Implementing a new system for managing a master sanitation schedule food manufacturing process can be a complex undertaking, particularly for large facilities with diverse cleaning requirements. To address this challenge, Weever software offers a structured rollout methodology that ensures seamless integration into existing operations. The platform provides manufacturers with pre-configured templates and workflows aligned with industry best practices, allowing them to start using the system immediately. At the same time, Weever's flexible design is configurable, enabling facilities to adapt the platform to their unique needs. During the rollout process, Weever provides comprehensive support to ensure a smooth transition. Training materials, user guides, and dedicated onboarding resources help teams quickly become proficient with the platform, minimizing disruption to daily operations. Once implemented, Weever software standardizes cleaning practices across the facility, ensuring consistency and efficiency in every aspect of sanitation management.
Transforming Food Production Through Smarter Cleaning Practices
Weever's software isn't just a tool for managing cleaning schedules-it's a solution for transforming the food and beverage manufacturing industry. By simplifying sanitation management, automating workflows, providing actionable insights, and ensuring smooth implementation, Weever helps manufacturers maintain the highest standards of food safety and maintenance management. The platform's ability to adapt to the specific needs of food production facilities ensures that every area and piece of equipment is cleaned and sanitized effectively, minimizing contamination risks and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Additionally, by leveraging data-driven insights and real-time reporting, manufacturers can continuously refine their master sanitation program, achieving greater efficiency and accountability over time.
Achieve Sanitation Excellence with Weever Software
Managing a food plant master sanitation schedule doesn't have to be a time-consuming, error-prone process. Weever software simplifies every aspect of sanitation management, from structuring cleaning schedules to tracking and optimizing performance. Whether you're looking to streamline the planned cleaning of food manufacturing activities or ensure consistent compliance with your master sanitation schedule, Weever is the solution you've been searching for.
Ready to see how Weever can revolutionize your approach to sanitation? Contact Weever today for a demo and discover the future of food safety and maintenance management.
Transform your sanitation process today. Schedule a demo with Weever.
Transform your sanitation process today. Schedule a demo with Weever.
Continue Reading
"Having cloud-based forms on devices around the facility makes them so much more accessible, which makes it painless for operators to quickly provide a report."
Johanna Velez, VP Quality Assurance


"Weever is really user friendly and will have a massive positive impact on our operations and training team."
Mel Cadle - Op Ex Lead Process Engineer


"It's shifted our safety culture because now we are much more focused on what we should be looking at."
Kody Crossen, Operations Manager of EHS