How Autonomous Maintenance Programs Work
Andy Pritchard | July 19, 2022 | 5 min read

Deciding that you’d like to implement Autonomous Maintenance in your plant is a great first step towards promoting a more efficient and profitable plant. Now you’re faced with the real challenge - how to begin?
The 7-Step Approach
In our experience with our clients, we’ve found the following 7-step approach, broken into 3 stages, works well. The process should be management-led with input from operators and supervisors. The 7-step approach focuses on progressively upgrading equipment and operator capabilities as you move forward, with each step being fully implemented before moving on to the next.
The process involves a bit of upfront time to get operators up to speed. Don’t rush! Taking your time and getting it right at the beginning will save you time and headaches down the road. In time, the program will begin to gain its own natural momentum.
STAGE 1: INITIATE
Establish basic equipment conditions and a system for sustaining them. Operators should be conscious of all elements of the CIL while performing one.

STEP 1: Increase Operator Knowledge
In order for operators to identify and proactively troubleshoot maintenance issues they should be trained on the equipment and the basics of how it works. Operators should understand the components and parts that fail due to wear and tear, how to identify when they need cleaning or lubrication, and basic troubleshooting.
Good examples of this type of practical knowledge include:
- How and when to tighten fasteners and bolts
- The replacement of oil and air filters
- Fluid replenishment
- Lubrication procedures
- And so on …
STEP 2: Initial Cleaning and Inspection
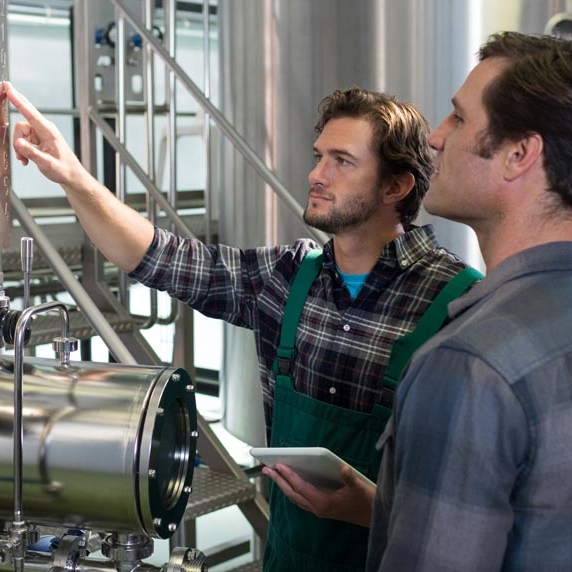
Partner your technicians with a small team of operators to do a full clean and inspection of your machinery. The purpose here is to build knowledge, build teamwork between your associates and maintenance staff, and bring the machine to an ideal state. This should include servicing inaccessible sections of the machine that regular cleaning won’t reach. Remember to include safety best practices like lockout/tagout (LOTO) to promote safety consciousness.
STEP 3: Eliminate Causes of Contamination
Now that your equipment is in peak operating condition, it's now your operator's responsibility to keep it that way. Good housekeeping practices and regular cleaning will proactively eliminate contamination that can accelerate deterioration.
STEP 4: Set Standards for Lubrication and Inspection
In addition to regular cleaning, equipment should be lubricated and maintained according to the manufacturer’s specs. This will help maintain its “like new” level of quality and performance. Set and reinforce standards on what components should be inspected and how to identify issues, what maintenance tasks are required, how to do them, and how often they should be done.
STAGE 2: EXPAND
Train operators on inspections and begin the process of performing basics maintenance activities autonomously.

STEP 5: Conduct Inspections and Monitor Results
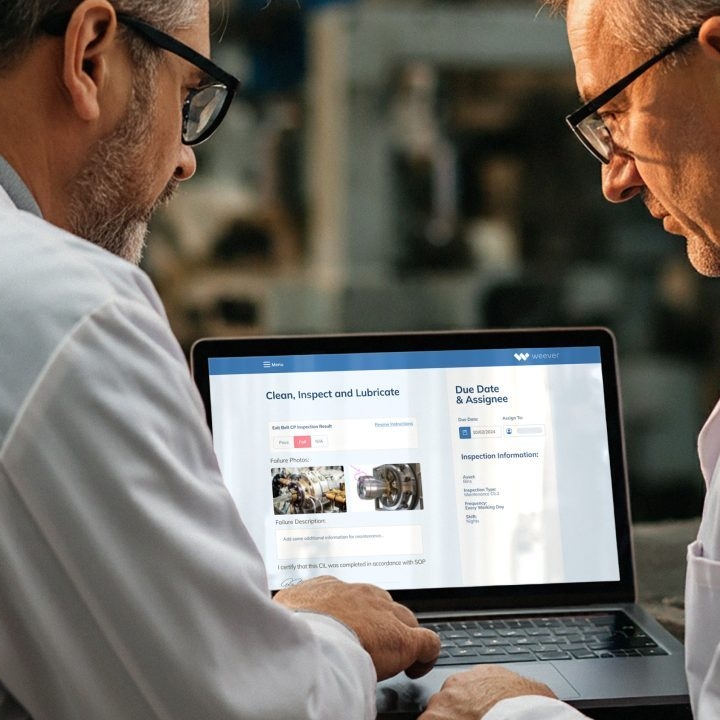
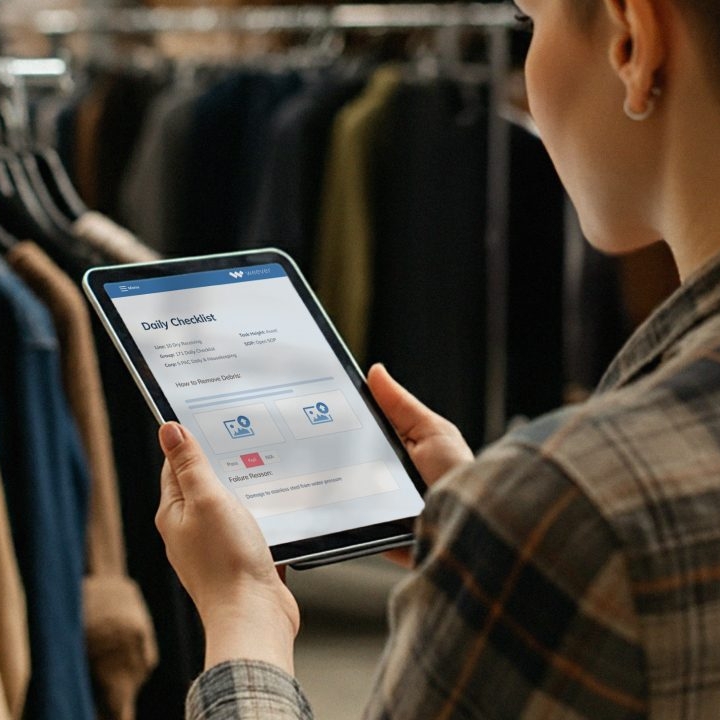
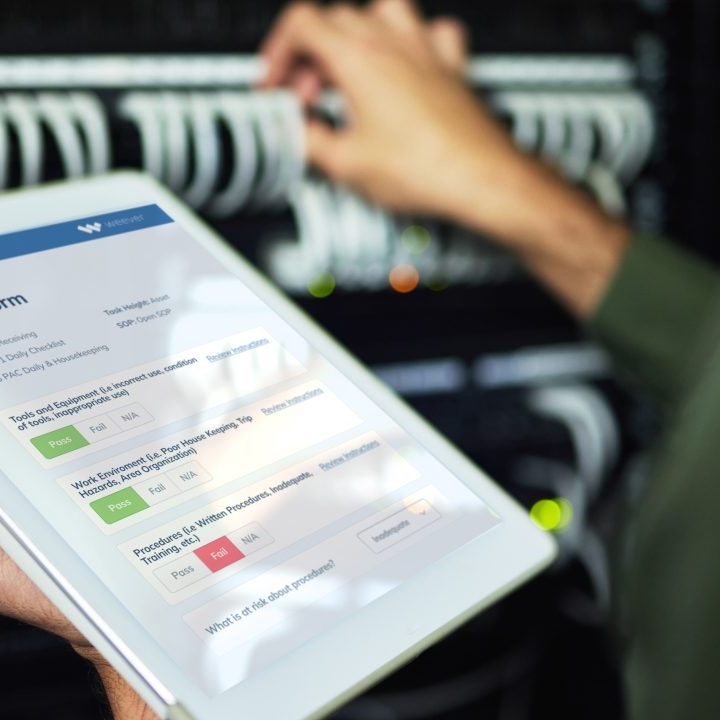
Once standards have been set, ensure they are being followed. Consider using a standardized CIL form that will allow you to capture and track ongoing or regular issues. Collect and review maintenance data regularly. This data will be invaluable for planning proactive maintenance by your technicians and refining your CIL standards over time. Leveraging a software solution can help streamline CIL and Centerline schedules.
STEP 6: Use Visual Maintenance Management
Consider using visual cues on equipment that will help your operators maintain the standards you set up in Step 4. Some examples of this are color-coding gauges to show ideal centerline values, clearly marking where inspections should be completed, visual reminders of safety procedures, etc. You can also use physical QR codes that link operators to the most recent documentation (such as machine manuals) and inspection forms.
STAGE 3: MAINTAIN AND IMPROVE
Complete the process of standardization and work towards perfecting operator maintenance skills.
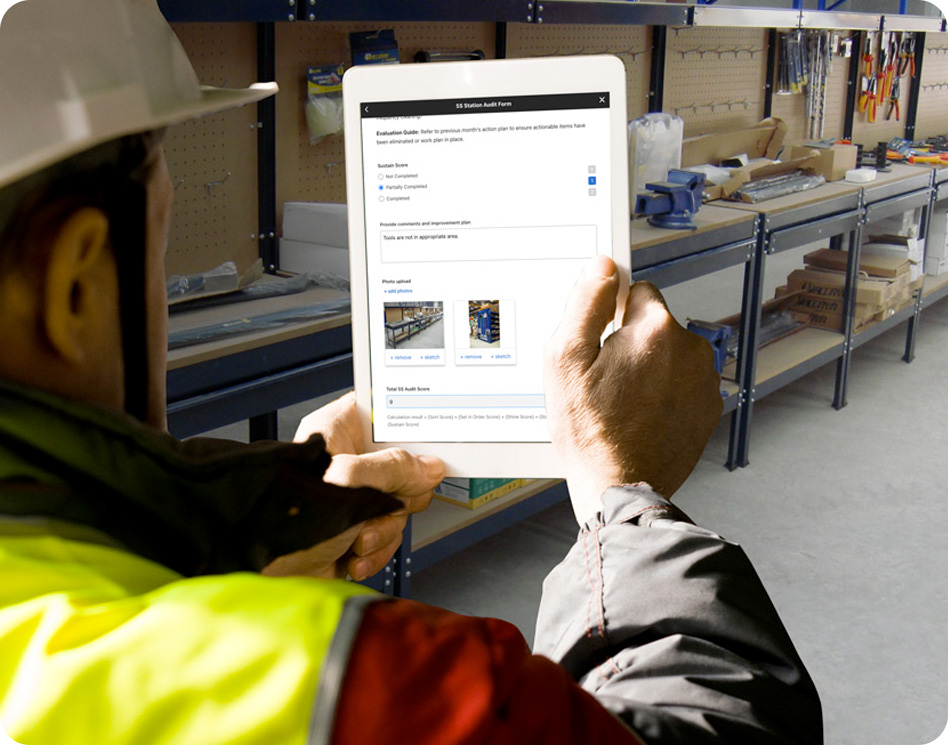

STEP 7: Incrementally Improve Over Time
The first steps toward Autonomous Maintenance should generate a lot of data, and the initial training may not include all possible points of failure. Get feedback from your operators, and make regular review and updates of your 5S, CIL, and Centerline procedures part of your new AM culture. Remember that your new Autonomous Maintenance program will be a work in progress. Give your team ample time as your staff adapts, standards are set, and valuable lessons are learned.
Continue Reading about Autonomous Maintenance
Ultimate Guide to Success with Autonomous Maintenance
Everything you need to know about how Autonomous Maintenance works and the best practices gleaned from our 10+ years of experience helping organizations achieve success.
Everything you need to know about how Autonomous Maintenance works and the best practices gleaned from our 10+ years of experience helping organizations achieve success.

bandjlogo

Bell-logo-New

Canadian-Tire-Logo

Diageo-customer-logo

greyston-bakery-logo

hello-fresh-customer

marks-customer-logo

CSL_Limited_logo

monin-logo

Winland Food

Mars-logo-main

rise-baking-customer-logo

Rockwool-Customer-Logo-min

Sportcheck-customer-logo

unilever-customer-logo

walmart-logo-small

husqvarna-customer-logo

Ajinomoto_logo

Peet's_Coffee_logo

Royal-Canin-Logo