Overview of Food Production Sanitation Regulations
Andy Pritchard | January 19, 2023 | 5 min read
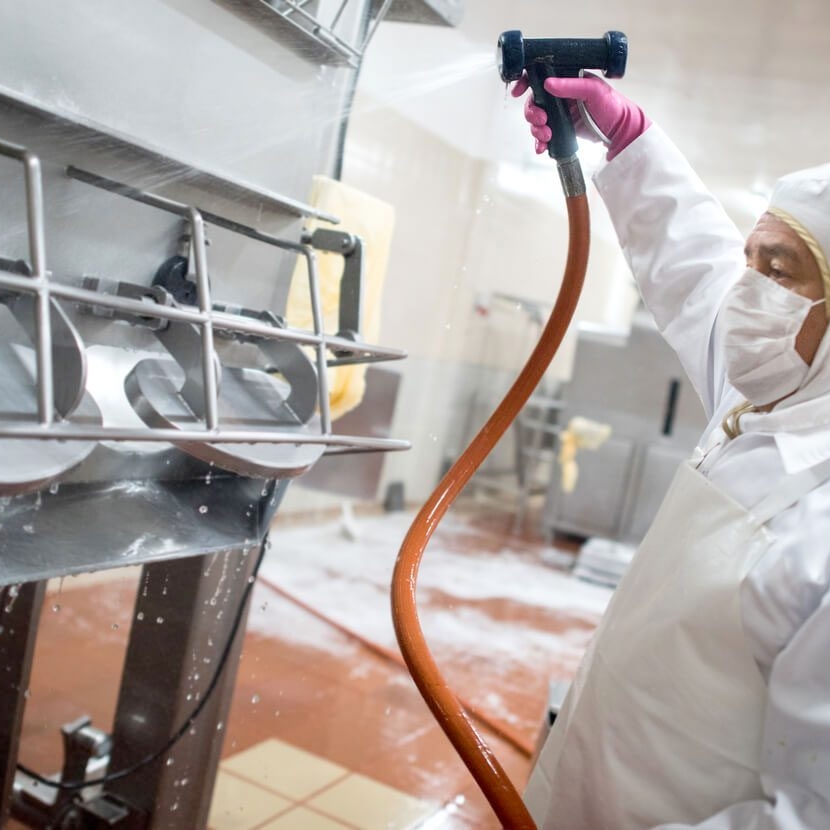

Outbreaks caused by poor line sanitation can cause long-term damage to the brand, cost hundred of thousand of dollars in recalls, lawsuits, and regulatory penalties, and result in employee engagement issues.
The Centers for Disease Control estimates that 48 million people get sick, 128,000 are hospitalized and 3,000 die from foodborne diseases in the United States each year.
Without proper sanitation, food plants cannot legally function and manufacture products. Proper sanitation means that the facility is fully clean where necessary, significantly reducing the risk of bacteria and other harmful pathogens from lingering and contaminating products.
Understanding the Regulations

USA Overview
In the United States, food plant production line sanitation is governed by several regulations and guidelines issued by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The main regulations are:
Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations: These regulations outline the general principles for food manufacturing and packaging to ensure the safety and quality of the food products. The cGMP regulations include requirements for sanitation, such as maintaining clean and sanitary facilities, equipment and utensils.
The Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) system: This is a preventive approach to food safety that focuses on identifying potential hazards in the food production process and implementing measures to prevent those hazards. HACCP requires food plants to conduct a hazard analysis, establish critical control points, implement monitoring procedures, and take corrective actions as necessary.
The Sanitary Transportation of Human and Animal Food regulation: This regulation requires shippers, loaders, carriers by motor or rail vehicle, and receivers engaged in the transportation of food to follow adequate sanitary practices to prevent the contamination of food.
The Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA): This law aims to modernize the food safety system in the United States and focuses on preventing food safety problems before they occur. FSMA requires food facilities to have written food safety plans, including preventive controls, to minimize the risk of foodborne illness.
These regulations and guidelines aim to ensure that food products are produced and transported under hygienic and safe conditions. Food plants are required to implement and maintain effective sanitation programs and keep detailed records to demonstrate compliance with the regulations. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in penalties, product recalls, and damage to a company's reputation.
Europe Overview
In Europe, the food production plant sanitation is governed by several regulations and guidelines issued by the European Union (EU). The main regulations are:
Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 on the hygiene of foodstuffs: This regulation sets out the general principles and requirements for the hygiene of food production. It requires food business operators to implement and maintain a permanent procedure based on HACCP principles, to ensure the safety and quality of food products.
Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 laying down specific rules for the organization of official controls on products of animal origin intended for human consumption: This regulation sets out the specific rules for the official controls on food of animal origin in the EU, including requirements for hygiene and sanitation of food establishments.
Regulation (EC) No 854/2004 laying down specific rules for the organization of official controls on products of plant origin intended for human consumption: This regulation sets out the specific rules for the official controls on food of plant origin in the EU, including requirements for hygiene and sanitation of food establishments.
Regulation (EC) No 882/2004 on official controls performed to ensure the verification of compliance with feed and food law, animal health and animal welfare rules: This regulation sets out the rules for official controls to be performed on feed and food and to ensure the compliance with the EU feed and food law, animal health and animal welfare rules.
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines: The EU GMP guidelines outline the general principles for food manufacturing and packaging to ensure the safety and quality of food products. The GMP guidelines include requirements for sanitation, such as maintaining clean and sanitary facilities, equipment, and utensils.
These regulations aim to ensure that food products are produced and processed under hygienic and safe conditions and to protect the health of consumers. Food production plants are required to implement and maintain effective sanitation programs, keep detailed records to demonstrate compliance with the regulations, and be subject to regular inspections by the authorities. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in penalties, product recalls, and damage to a company's reputation.
In response to a growing number of foodborne illness outbreaks, the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) of 2011 shifted the focus from responsive contamination management to preventing food safety problems before they occur and recognizes the importance of strong foodborne illness and outbreak surveillance systems. The FSMA act seeks to protect public health more effectively by strengthening the food safety system.
The major elements of the FSMA can be separated into five key areas:
- Preventive Controls
- Inspection and Compliance
- Imported Food Safety
- Response
- Enhanced Partnerships
The USDA’s HACCP regulation puts sanitation in its proper perspective: Sanitation maintains or restores a state of cleanliness and promotes hygiene for the prevention of foodborne illness.
Sanitation is an essential prerequisite program for food safety. The Preventive Controls Regulation for Human Food found in 21 CFR Part 117 further underscores the importance of this element. Preventive controls are defined as:
“…those risk-based, reasonably appropriate procedures, practices and processes that a person knowledgeable about the safe manufacturing, processing, packing or holding of food would employ to significantly minimize or prevent the hazards identified under the hazard analysis that are consistent with the current scientific understanding of safe food manufacturing, processing, packing or holding at the time of the analysis.”
The regulation establishes the following preventive controls:
- Process
- Allergen
- Sanitation
- Supply Chain
- Recall
- Other

21 CFR Part 117.135 (c) 3 specifically addresses sanitation preventive controls and may be seen below:
(3) Sanitation controls. Sanitation controls include procedures, practices and processes to ensure that the facility is maintained in a sanitary condition adequate to significantly minimize or prevent hazards such as environmental pathogens, biological hazards due to employee handling, and food allergen hazards. Sanitation controls must include, as appropriate to the facility and the food, procedures, practices and processes for the:
(i) Cleanliness of food-contact surfaces, including food-contact surfaces of utensils and equipment;
(ii) Prevention of allergen cross-contact and cross-contamination from insanitary objects and from personnel to food, food packaging material, and other food-contact surfaces and from raw product to processed product.
______
Cleaning and Sanitation is a legal requirement for any organization involved in food and beverage manufacturing because it helps to prevent food pathogen outbreaks. Although everyone does it, there are a variety of different ways to clean your lines to consider. Good cleaning practices can have a positive impact on your product quality, your brand and the engagement of your employees.

How-to instructions, best practices, and customer stories to help you set up and optimize your cleaning and sanitation program.
How-to instructions, best practices, and customer stories to help you set up and optimize your cleaning and sanitation program.

bandjlogo

Bell-logo-New

Canadian-Tire-Logo

Diageo-customer-logo

greyston-bakery-logo

hello-fresh-customer

marks-customer-logo

CSL_Limited_logo

monin-logo

Winland Food

Mars-logo-main

rise-baking-customer-logo

Rockwool-Customer-Logo-min

Sportcheck-customer-logo

unilever-customer-logo

walmart-logo-small

husqvarna-customer-logo

Ajinomoto_logo

Peet's_Coffee_logo

Royal-Canin-Logo
Learn more about Sanitation ...
Weever is a comprehensive operations management platform that is used to automate safety, quality, maintenance, production, compliance, continuous improvement and training operational requirements.