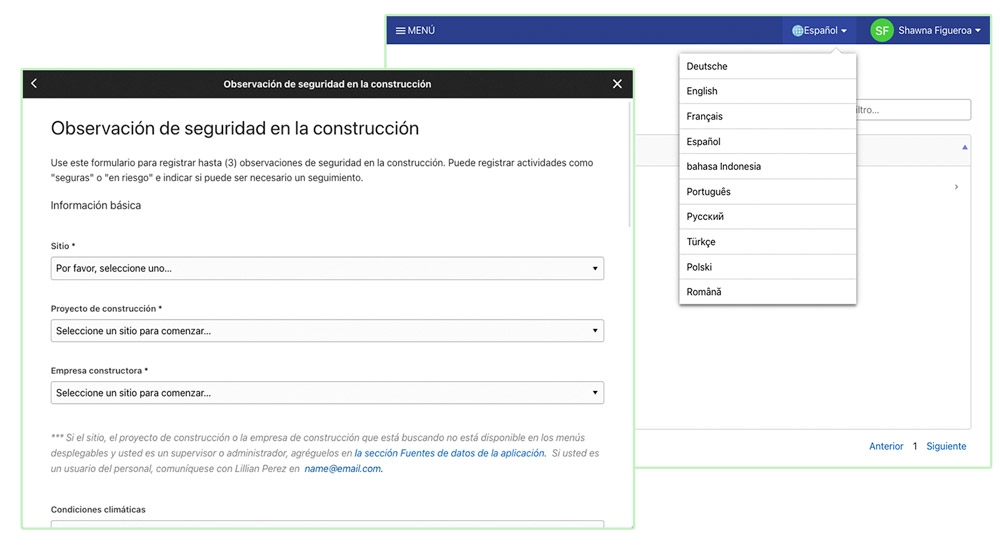
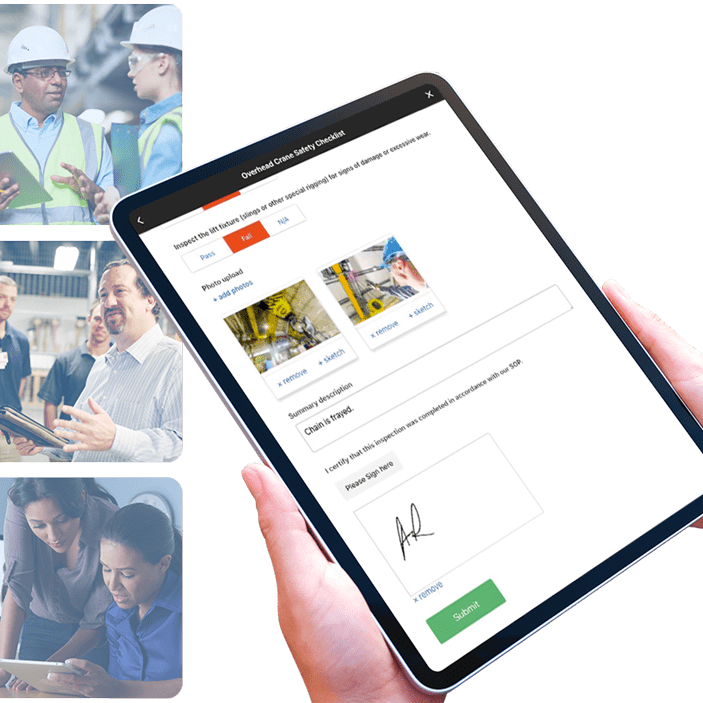
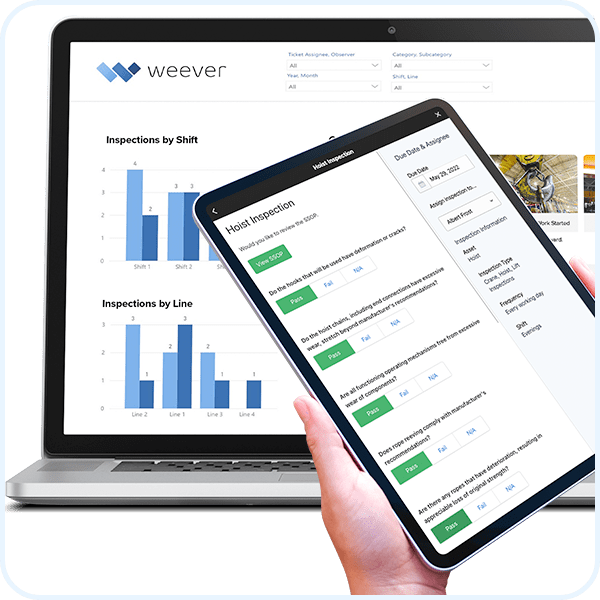
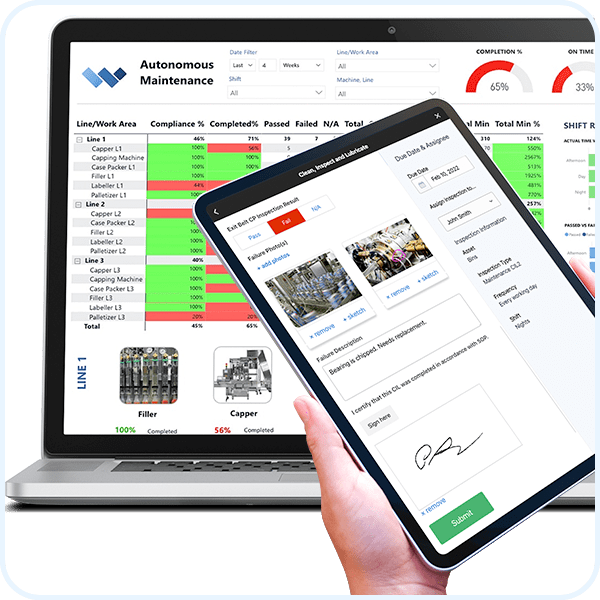
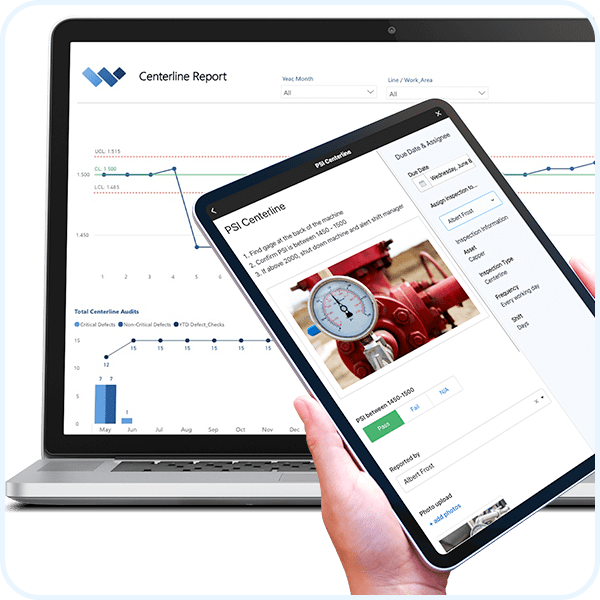
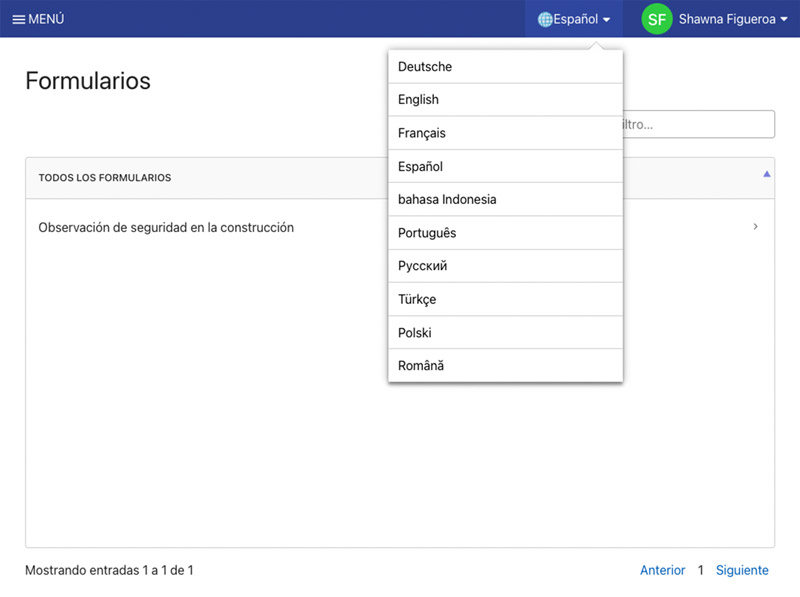
What is Software Localization?
Andy Pritchard | April 6, 2022 | 5 min read

bandjlogo

Bell-logo-New

Canadian-Tire-Logo

Diageo-customer-logo

greyston-bakery-logo

hello-fresh-customer

marks-customer-logo

CSL_Limited_logo

monin-logo

Winland Food

Mars-logo-main

rise-baking-customer-logo

Rockwool-Customer-Logo-min

Sportcheck-customer-logo

unilever-customer-logo

walmart-logo-small

husqvarna-customer-logo

Ajinomoto_logo

Peet's_Coffee_logo

Royal-Canin-Logo