Predictive vs. Preventive Maintenance: Which is Better for Manufacturers?
Compare predictive and preventive maintenance for manufacturing efficiency.
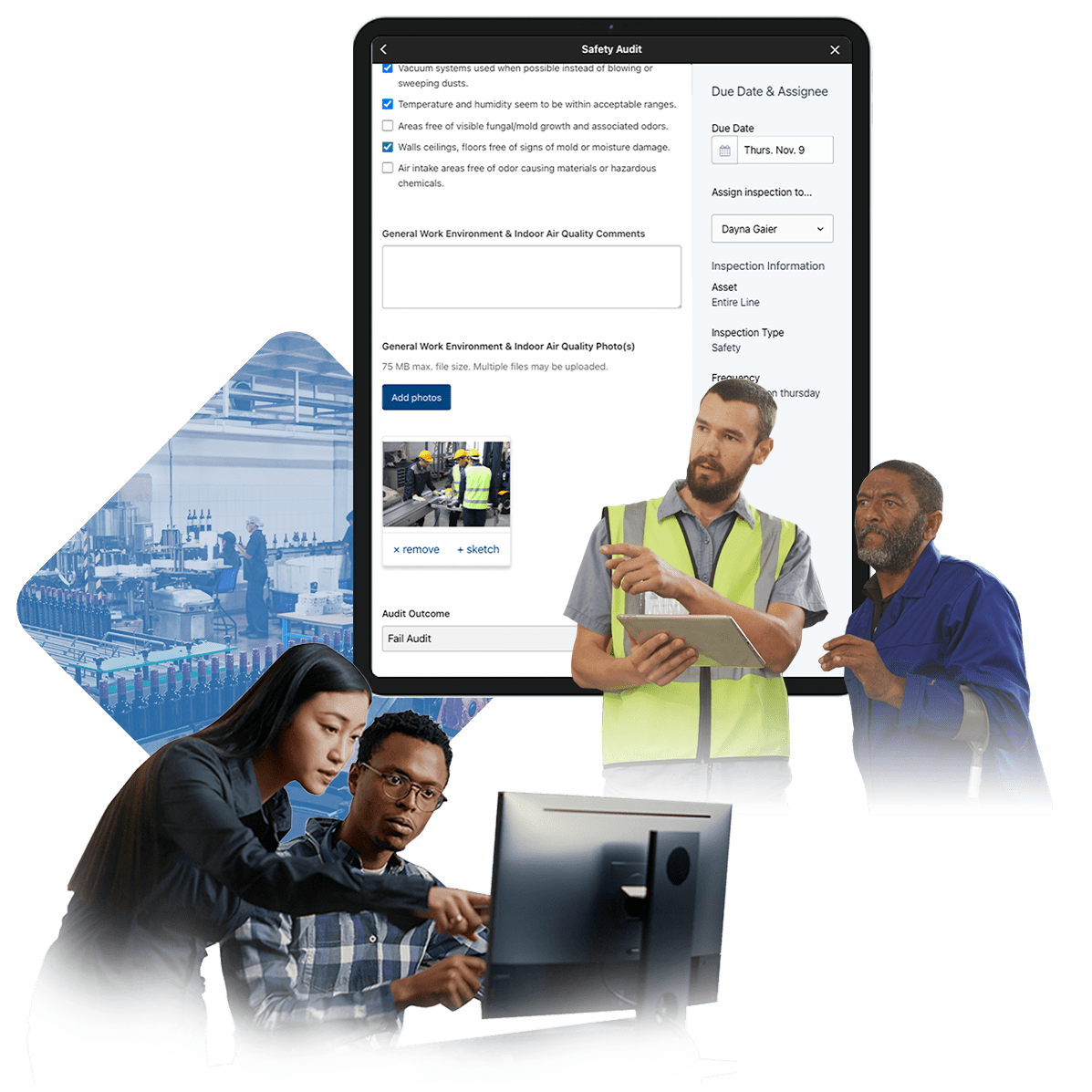
Effective maintenance strategies are crucial in the manufacturing industry to ensure operational efficiency, minimize downtime, and extend the lifespan of equipment. Effective maintenance involves more than just addressing issues as they arise; it also focuses on proactively avoiding them altogether. In today's ever-evolving technological landscape, manufacturers are fortunate to have a wide array of advanced maintenance solutions at their disposal. These cutting-edge tools have the potential to greatly optimize and improve their operations. Two of the most effective strategies in the field are preventive and predictive maintenance.
Regular, scheduled maintenance tasks are essential for preventing equipment failures before they occur. This approach is based on the concept of regularly servicing equipment at set intervals, regardless of its current state. On the other hand, predictive maintenance utilizes cutting-edge technologies such as IoT sensors and data analytics to continuously monitor equipment and anticipate potential failures in advance. By assessing the real-time condition of the equipment, maintenance can be carried out as and when required, eliminating unnecessary procedures.
Let’s explore and analyze the differences between predictive and preventive maintenance strategies, shedding light on the advantages of both approaches. Through a thorough analysis of these two approaches, our goal is to equip manufacturers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions about the maintenance strategy that aligns best with their unique operational requirements.
Understanding Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is a proactive approach to maintaining equipment and machinery in manufacturing environments. It involves regularly scheduled maintenance tasks aimed at preventing equipment failures and extending the lifespan of assets. Unlike reactive maintenance, which addresses issues after they occur, preventive maintenance seeks to address potential problems before they result in downtime or costly repairs.
Key Features and Common Practices
Preventive maintenance is characterized by its routine and systematic approach. Key features include:
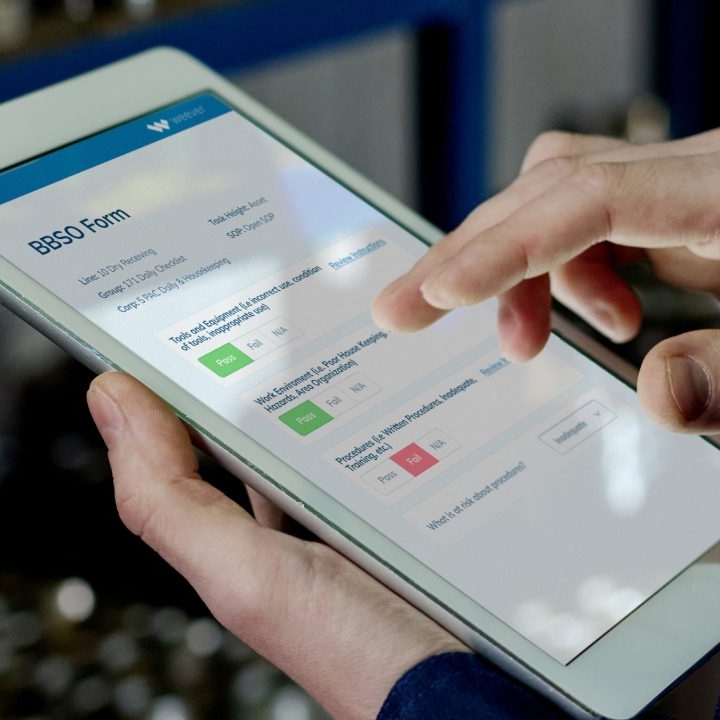
- Scheduled Inspections and Servicing: Maintenance tasks are performed at regular intervals based on time, usage, or equipment condition. This can include tasks such as lubricating moving parts, checking fluid levels, and inspecting components for wear and tear.
- Standardized Procedures: Maintenance activities follow a set of standardized procedures to ensure consistency and thoroughness. This includes detailed checklists and protocols that technicians must adhere to during each maintenance cycle.
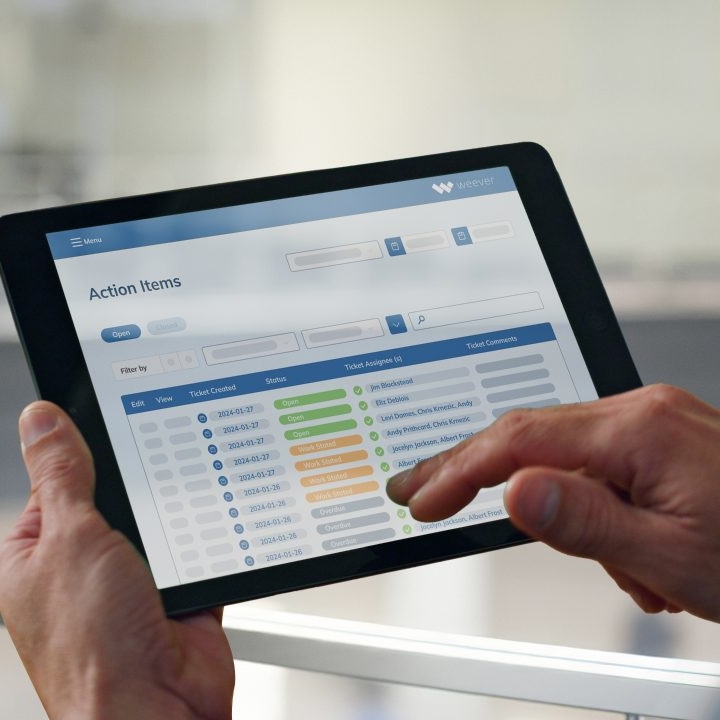
- Documentation and Tracking: Detailed records are kept of all maintenance activities. This documentation helps track the history of equipment maintenance, identify recurring issues, and plan future maintenance tasks more effectively.
- Replacement of Worn Parts: Parts that are prone to wear and tear are replaced at regular intervals, even if they have not yet failed. This preemptive approach helps avoid unexpected breakdowns and extends the overall life of the equipment.
Benefits of Preventive Maintenance for Manufacturers
Implementing a preventive maintenance strategy offers several benefits for manufacturers:
- Reduced Downtime: By addressing potential issues before they lead to equipment failure, preventive maintenance helps minimize unplanned downtime. This ensures that production processes run smoothly and efficiently.
- Scheduled Maintenance Tasks: Maintenance activities are planned and scheduled in advance, allowing manufacturers to allocate resources and personnel more effectively. This organized approach reduces the impact of maintenance on production schedules.
- Prolonged Equipment Life: Regular maintenance helps keep equipment in optimal condition, reducing the wear and tear that can lead to premature failure. As a result, the lifespan of machinery and equipment is extended, providing a better return on investment.
Overall, preventive maintenance is a proactive and systematic approach that helps manufacturers maintain high levels of productivity, minimize operational disruptions, and ensure the longevity of their equipment. By implementing preventive maintenance practices, manufacturers can achieve more reliable and efficient operations, ultimately contributing to their bottom line.
Exploring Predictive Maintenance and its Usage in Manufacturing
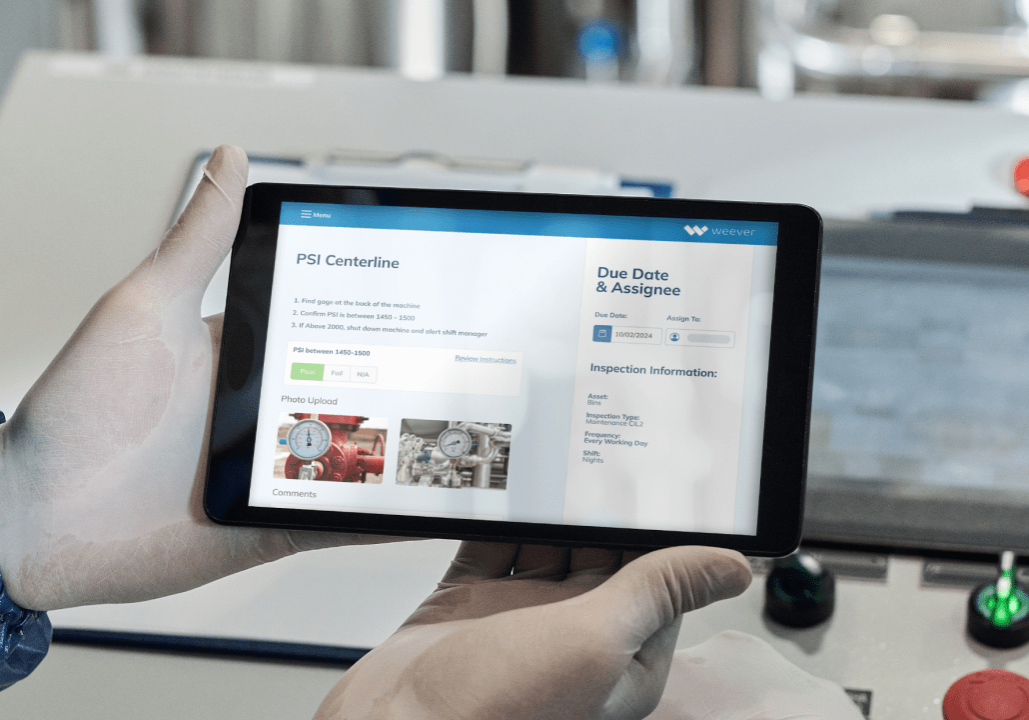
Predictive maintenance represents a significant advancement in the field of equipment maintenance, leveraging modern technology to predict and prevent equipment failures before they occur. Unlike preventive maintenance, which follows a schedule, predictive maintenance relies on the actual condition of equipment to determine when maintenance should be performed.
Key Features and Technologies Involved
Predictive maintenance employs a variety of advanced technologies to monitor and analyze equipment performance:
- IoT Sensors: These sensors are embedded in machinery to collect real-time data on various parameters such as temperature, vibration, and pressure. This data provides valuable insights into the equipment's current state.
- Data Analytics: Collected data is processed and analyzed using sophisticated algorithms. By examining patterns and trends, data analytics can identify early signs of potential issues that might not be apparent through routine inspections.
- Machine Learning: Predictive maintenance systems often utilize machine learning to improve their predictive capabilities over time. These systems learn from historical data to make increasingly accurate predictions about equipment health and potential failures.
- Integration with Maintenance Management Software: Solutions like Weever's maintenance software play a crucial role in predictive maintenance. Weever integrates with IoT sensors and analytics tools to provide a comprehensive view of equipment health, enabling manufacturers to make data-driven maintenance decisions.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance for Manufacturers
Implementing predictive maintenance offers several substantial benefits for manufacturers:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of equipment conditions allows for immediate detection of anomalies. This real-time insight enables manufacturers to respond swiftly to potential issues, preventing minor problems from escalating into major failures.
- Early Detection of Potential Issues: By identifying signs of wear and tear or other problems early on, predictive maintenance helps address issues before they lead to equipment downtime. This proactive approach ensures that maintenance is performed only when necessary, based on actual equipment needs.
- Optimized Maintenance Schedules: Predictive maintenance allows for the optimization of maintenance schedules. Instead of adhering to a rigid schedule, maintenance activities can be planned based on the real-time condition of the equipment. This flexibility reduces unnecessary maintenance tasks and allocates resources more efficiently.
- Enhanced Equipment Lifespan: By addressing potential issues early and maintaining equipment in optimal condition, predictive maintenance can significantly extend the life of machinery. This results in better asset utilization and a higher return on investment.
Weever's software enhances these benefits enables manufacturers to harness the full potential of predictive maintenance, ensuring that their operations remain efficient, reliable, and cost-effective. With Weever, manufacturers can transform their maintenance strategies, moving from a reactive or preventive approach to a more sophisticated and proactive predictive maintenance model.
Preventative Maintenance Plays a Vital Role in Maximizing Efficiency for Manufacturers
One of the advantages of this solution is that it helps minimize downtime, ensures well-planned maintenance schedules, and extends the lifespan of machinery. Utilizing cutting-edge technologies like IoT sensors, data analytics, and machine learning, predictive maintenance keeps a constant watch on equipment, detecting and anticipating potential issues in real-time. This strategy provides a range of advantages such as the ability to monitor in real-time, identify issues early on, optimize maintenance schedules, and extend the lifespan of equipment.
Both maintenance strategies have their strengths and can be highly effective in various manufacturing environments. For manufacturers seeking a structured and routine approach to maintenance, preventive maintenance is a suitable option. It is effective in environments where equipment operates under stable conditions and where planned maintenance can be easily accommodated. For manufacturers looking to take a more dynamic and data-driven approach, predictive maintenance is the way to go. Solutions like Weever's software can greatly facilitate this process. In environments with varying equipment conditions, real-time monitoring can offer significant operational advantages.
Ultimately, the decision between preventive and predictive maintenance relies on the unique requirements and situations of each manufacturer. Through a thorough analysis of operational requirements, resource availability, and technological capabilities, manufacturers can identify the maintenance strategy that best suits their goals. Adopting the right maintenance approach can significantly improve equipment reliability and efficiency, leading to overall business success.
Transform Your Manufacturing Performance: Understand Predictive vs. Preventive Maintenance
Transform Your Manufacturing Performance: Understand Predictive vs. Preventive Maintenance
Continue Reading
"Having cloud-based forms on devices around the facility makes them so much more accessible, which makes it painless for operators to quickly provide a report."
Johanna Velez, VP Quality Assurance


"Weever is really user friendly and will have a massive positive impact on our operations and training team."
Mel Cadle - Op Ex Lead Process Engineer


"It's shifted our safety culture because now we are much more focused on what we should be looking at."
Kody Crossen, Operations Manager of EHS