Autonomous Maintenance in World Class Manufacturing
At Weever Apps, we’ve seen firsthand how Autonomous Maintenance in World Class Manufacturing (WCM) transforms production floors. This approach empowers operators to take ownership of their equipment, leading to improved efficiency and reliability.
Autonomous Maintenance WCM is more than just a buzzword; it’s a game-changer for modern manufacturing. In this post, we’ll explore its key components, implementation strategies, and the significant impact it can have on your operations.
What is Autonomous Maintenance?
Redefining Operator Roles
Autonomous Maintenance stands as a cornerstone of World Class Manufacturing, placing equipment care directly in operators’ hands. This approach transforms traditional production floor roles, making operators the primary defense against equipment failures and inefficiencies.
Operators don’t merely run machines; they develop an intimate familiarity with them. They perform daily cleaning, inspection, and basic maintenance tasks. This hands-on approach enables them to identify potential issues before they escalate into costly breakdowns.
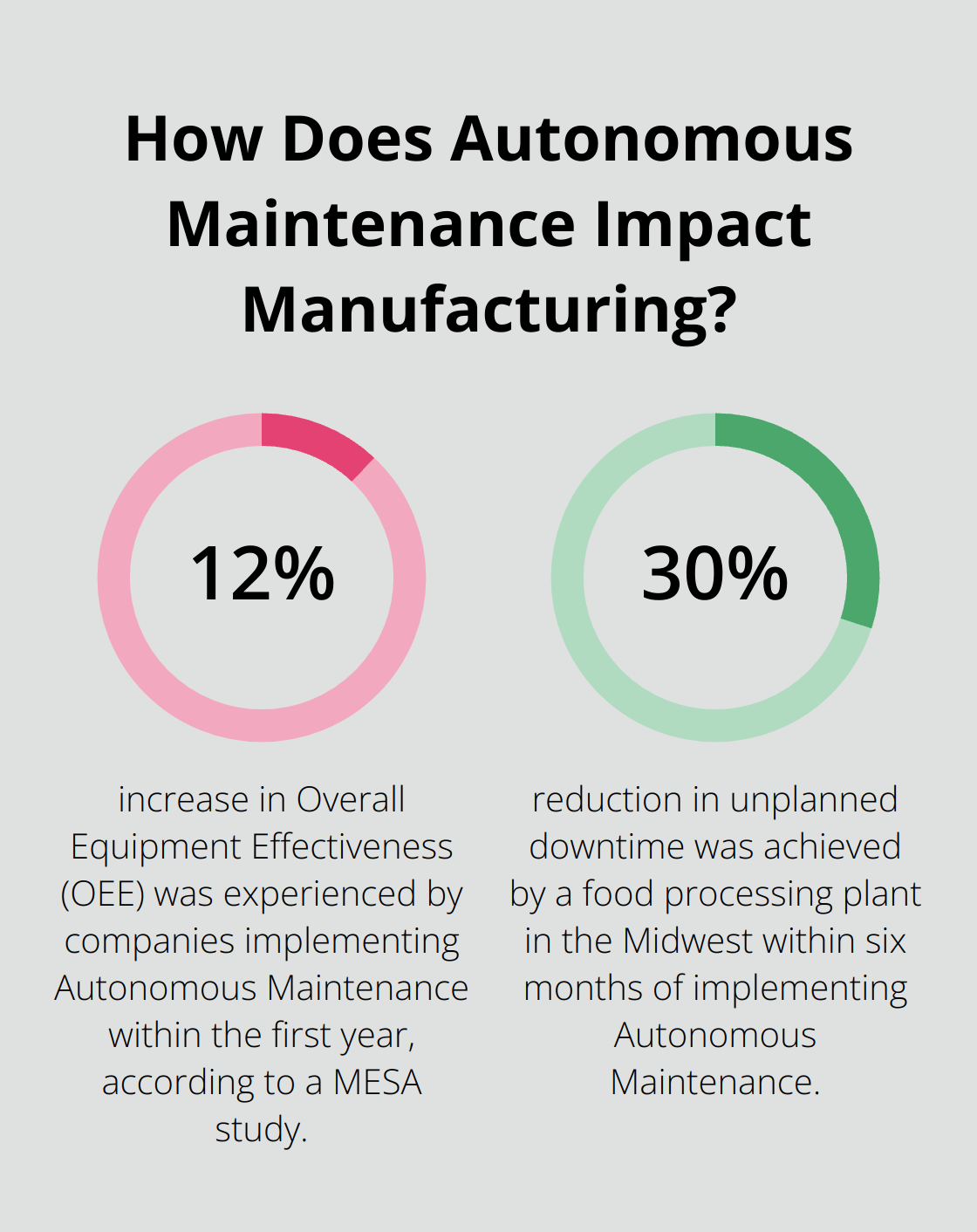
A Manufacturing Enterprise Solutions Association (MESA) study revealed that companies implementing Autonomous Maintenance experienced a 12% increase in Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) within the first year. This performance boost directly translates to improved productivity and reduced downtime.
Fostering Collaboration Between Operations and Maintenance
Autonomous Maintenance eliminates traditional silos between operations and maintenance departments. It creates a collaborative environment where operators and maintenance technicians unite to keep equipment running smoothly.
This collaboration proves crucial. The Aberdeen Group reports that top-performing manufacturers are 2.5 times more likely to implement cross-functional teams for equipment maintenance. These teams respond faster to issues and implement improvements more effectively.
Fueling Continuous Improvement
Autonomous Maintenance plays a powerful role in continuous improvement. As operators become more familiar with their equipment, they position themselves to suggest and implement enhancements.
A food processing plant in the Midwest implemented Autonomous Maintenance and achieved a 30% reduction in unplanned downtime within six months. The key to success? Empowering operators to make small, incremental improvements to their daily routines and equipment care practices.
Leveraging Digital Tools
Digital tools can supercharge Autonomous Maintenance programs. Modern platforms allow operators to easily log maintenance activities, report issues, and access critical equipment information – all from their mobile devices. This real-time data flow ensures that both operators and maintenance teams have the information they need to make quick, informed decisions.
Creating a Culture of Ownership
Autonomous Maintenance extends beyond keeping machines operational; it fosters a culture of ownership and continuous improvement on the shop floor. When implemented effectively, it leads to significant gains in productivity, equipment reliability, and overall operational excellence.
As we move forward, let’s explore the key components that make Autonomous Maintenance a powerful force in World Class Manufacturing.
Mastering the Core Elements of Autonomous Maintenance
Empowering Operators as Equipment Experts
Autonomous Maintenance transforms operators into equipment experts. This shift extends beyond basic training; it cultivates a deep understanding of machinery. Manufacturers should continually reduce equipment downtime and increase availability through the establishment of a preventive/predictive maintenance program.

Manufacturers should:
- Provide comprehensive training on equipment functionality and common issues
- Encourage operators to document observations and insights
- Create mentorship programs pairing experienced operators with newcomers
- Recognize operators who demonstrate exceptional equipment knowledge
Establishing a Rigorous Cleaning and Inspection Routine
Regular cleaning and inspection form the foundation of Autonomous Maintenance. Plants that implement daily cleaning and inspection routines can significantly reduce unexpected breakdowns.
Effective routines include:
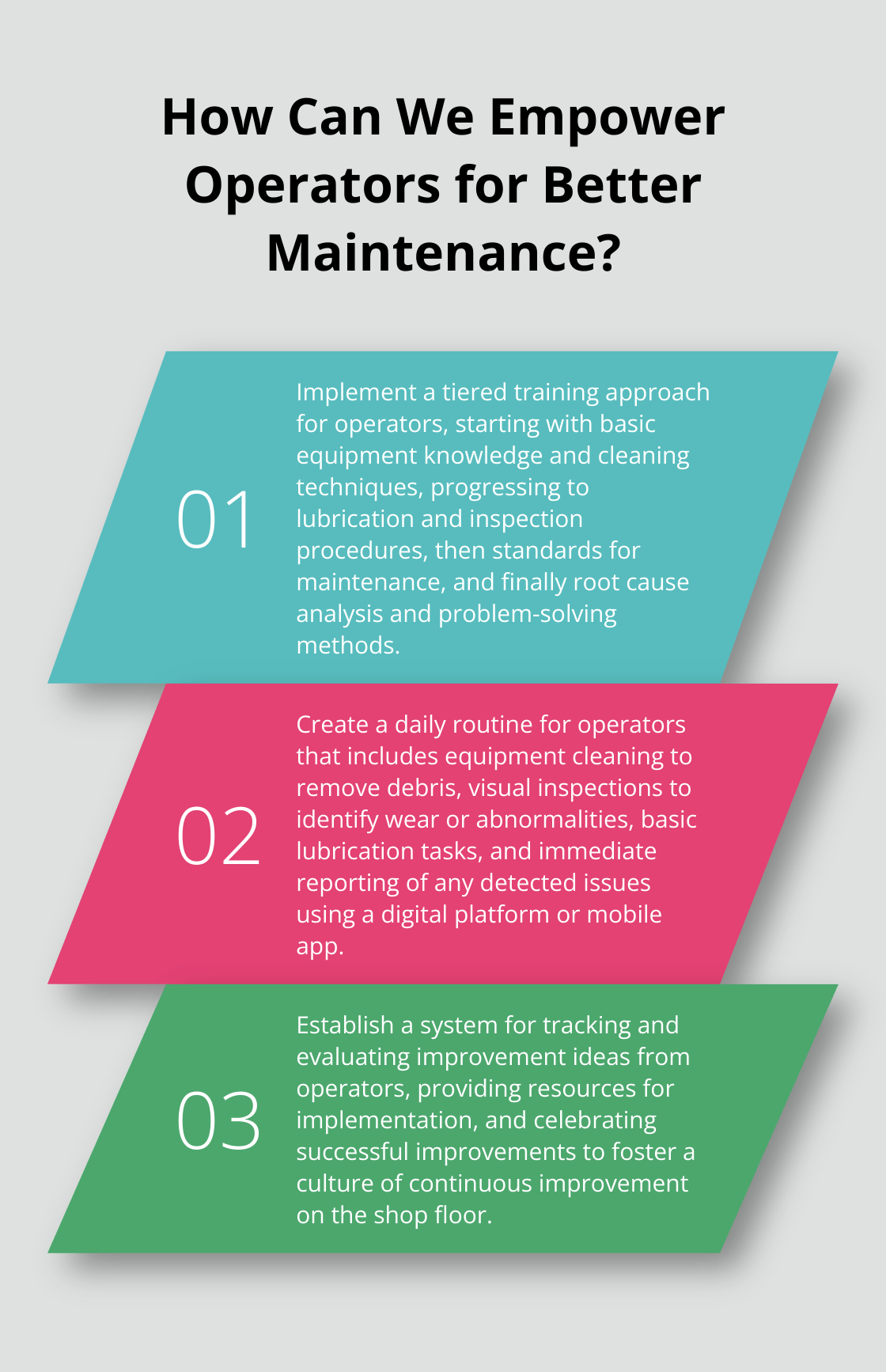
- Daily equipment cleaning to remove debris and contaminants
- Visual inspections to identify wear, loose parts, or abnormalities
- Basic lubrication tasks to maintain optimal equipment performance
- Immediate reporting of any detected issues or anomalies
Standardizing Procedures for Consistency and Efficiency
Standardization ensures consistent application of Autonomous Maintenance practices across the organization.
To standardize effectively:
- Develop clear, step-by-step procedures for each maintenance task
- Create visual aids and checklists to guide operators through processes
- Review and update procedures regularly based on feedback and results
- Use digital tools to ensure easy access to the latest procedures
Fostering a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Autonomous Maintenance thrives in an environment of continuous improvement.
To nurture this culture:
- Encourage operators to suggest improvements to equipment and processes
- Implement a system for tracking and evaluating improvement ideas
- Celebrate successful improvements and share lessons learned
- Provide resources and support for operators to implement their ideas
These core elements unlock the full potential of Autonomous Maintenance. Digital tools (such as those offered by Weever) support these efforts by providing platforms for procedure standardization, real-time issue reporting, and tracking improvement initiatives. The next chapter will explore the practical steps to implement Autonomous Maintenance in your organization, ensuring a smooth transition and maximum benefits.
How to Implement Autonomous Maintenance
Assess Current Practices
The first step to implement Autonomous Maintenance is to conduct a thorough assessment of current maintenance practices. This involves an analysis of equipment performance data, a review of existing maintenance procedures, and identification of areas where operator involvement can make the most significant impact.
A study by the Manufacturing Enterprise Solutions Association (MESA) found that companies who conducted comprehensive assessments before implementation saw a 15% higher success rate in their Autonomous Maintenance programs.
Secure Organizational Buy-In
To secure buy-in from both management and frontline workers, demonstrate the potential benefits of Autonomous Maintenance, such as reduced downtime and increased productivity. A study by Aberdeen Group, an IT research company, shows that businesses with strong leadership support for initiatives are more likely to meet their higher-level needs in Maslow’s hierarchy.
Develop Comprehensive Training Programs
Effective training is essential for the success of Autonomous Maintenance. Create a comprehensive training program that covers equipment functionality, basic maintenance techniques, and problem-solving skills.
The Japan Institute of Plant Maintenance recommends a tiered training approach:
- Basic equipment knowledge and cleaning techniques
- Lubrication and inspection procedures
- Standards for maintenance and equipment care
- Root cause analysis and problem-solving methods
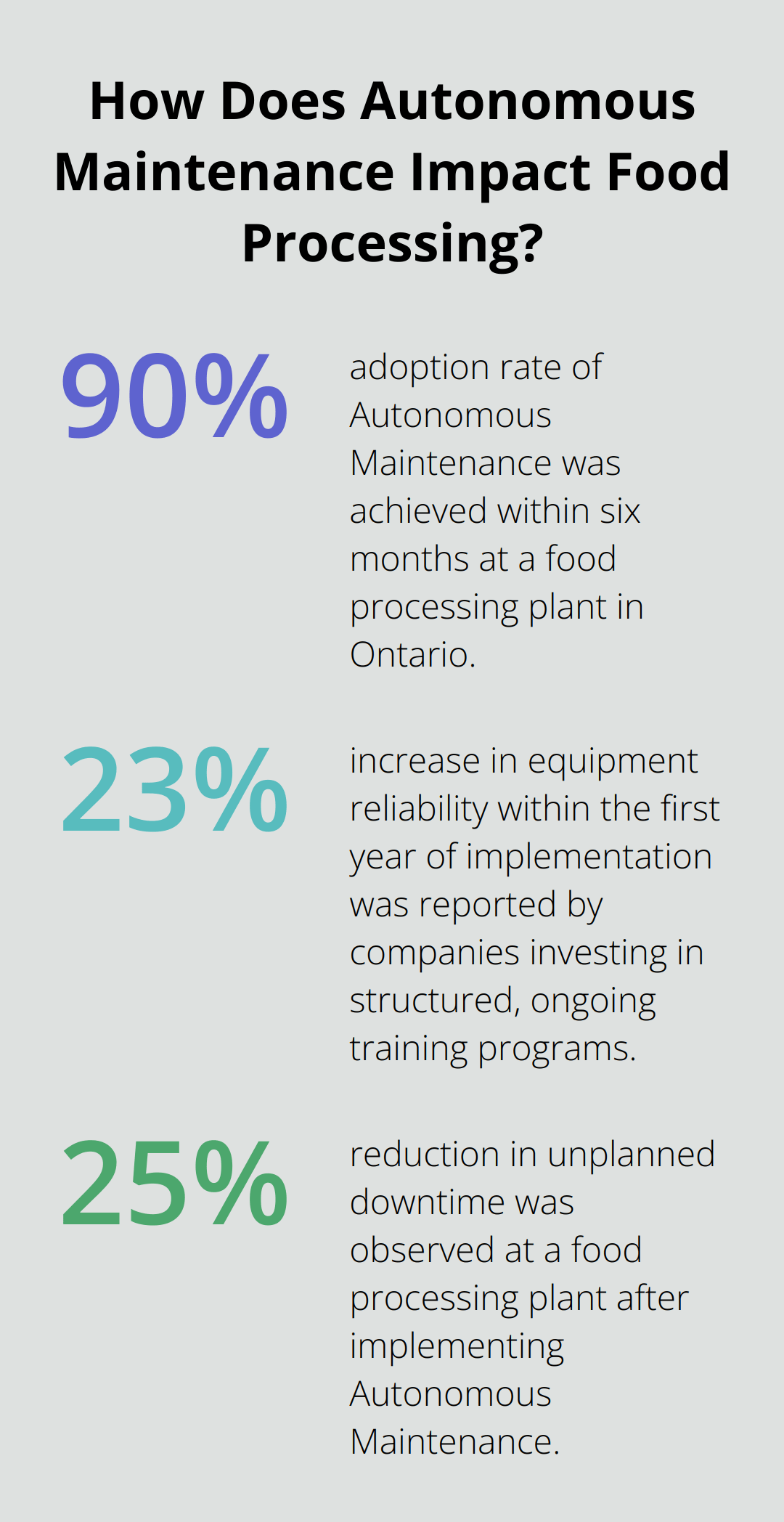
Companies that invest in structured, ongoing training programs report a 23% increase in equipment reliability within the first year of implementation (according to a survey by Plant Engineering magazine).
Integrate Digital Tools
Digital tools play a key role in modern Autonomous Maintenance implementations. Mobile applications and IoT sensors streamline data collection, automate work order generation, and provide real-time equipment performance insights.
Connected Worker platforms (such as Weever) allow operators to easily log maintenance activities, access equipment manuals, and report issues in real-time. This level of digital integration can reduce administrative work by up to 30% and improve response times to equipment issues by 40%.
Address Implementation Challenges
Resistance to change is a common hurdle in Autonomous Maintenance implementations. To address this, create a communication plan that clearly outlines the benefits of the new approach. Highlight early wins and success stories to build momentum.
A food processing plant in Ontario faced initial skepticism from operators when implementing Autonomous Maintenance. The plant involved operators in the planning process and recognized their contributions. As a result, they achieved a 90% adoption rate within six months and saw a 25% reduction in unplanned downtime.
To maintain consistency across shifts and departments, implement standardized procedures and regular audits. The Society for Maintenance and Reliability Professionals recommends quarterly audits to ensure adherence to Autonomous Maintenance practices.
Final Thoughts
Autonomous Maintenance in World Class Manufacturing (WCM) transforms modern production environments. Organizations empower operators to take ownership of their equipment, which leads to significant improvements in productivity and equipment reliability. Companies that implement this approach report Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) increases of up to 15% within the first year.
The integration of digital technologies enhances the effectiveness of Autonomous Maintenance programs. These tools provide real-time data insights, streamline communication, and enable more proactive maintenance strategies. Our Connected Worker platform supports Autonomous Maintenance initiatives by enabling operators to log activities, access information, and report issues in real-time.
The future of Autonomous Maintenance WCM will become more data-driven and predictive. Machine learning algorithms will analyze equipment performance data to predict potential failures before they occur. This shift towards predictive maintenance will reduce unplanned downtime and extend equipment lifespan (a key goal of WCM).