Benefits of Autonomous Maintenance: Why Implement It?
At Weever Apps, we’ve seen firsthand how autonomous maintenance can transform manufacturing operations. This approach empowers operators to take ownership of their equipment, leading to significant improvements in reliability and efficiency.
The benefits of autonomous maintenance extend far beyond just keeping machines running smoothly. In this post, we’ll explore how this strategy can boost productivity, cut costs, and create a more engaged workforce.
What Is Autonomous Maintenance?
A Shift in Maintenance Philosophy
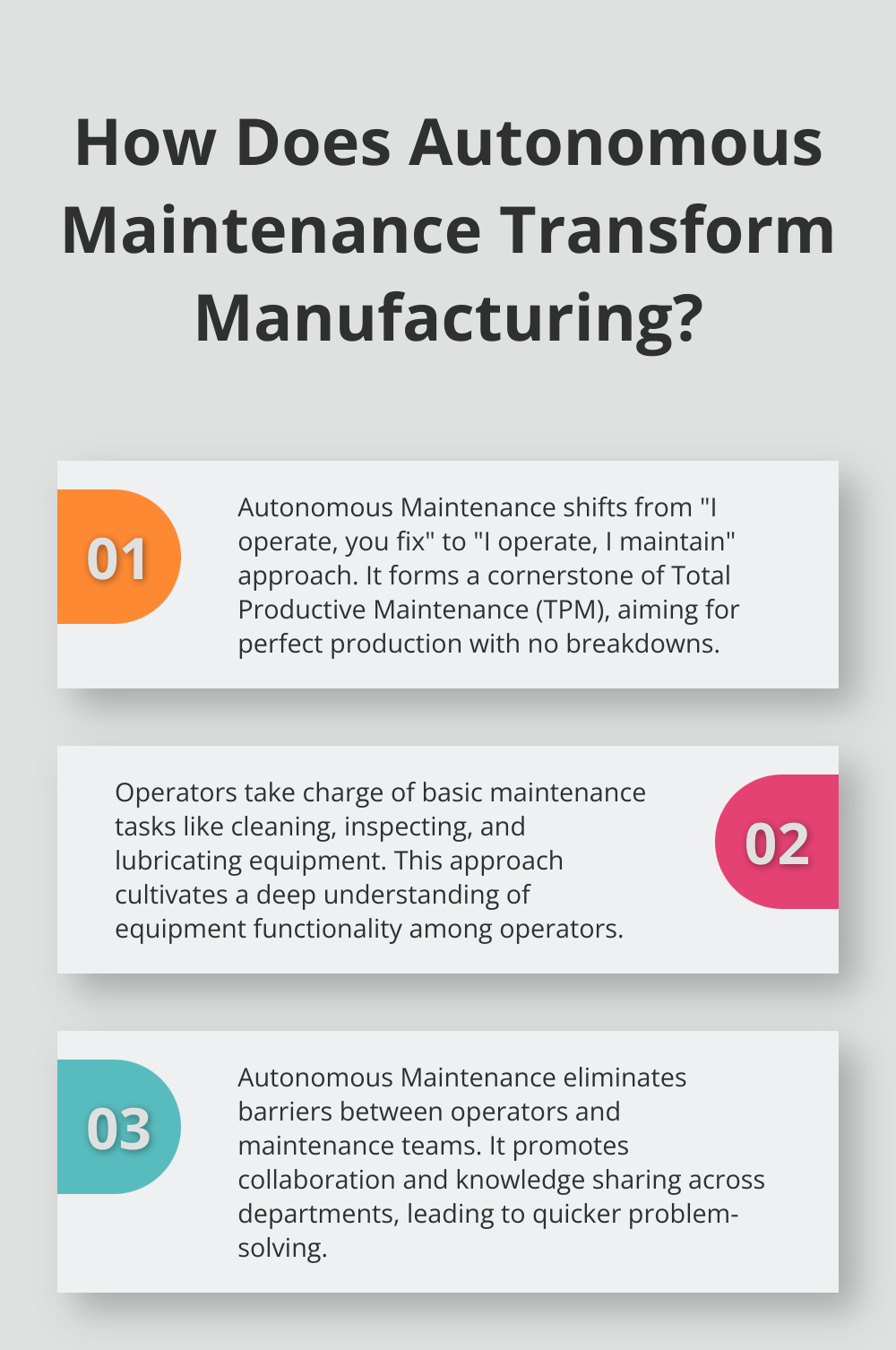
Autonomous Maintenance transforms the traditional “I operate, you fix” mentality into a collaborative “I operate, I maintain” approach. This strategy forms a cornerstone of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), a holistic approach to equipment maintenance that strives to achieve perfect production with no breakdowns or small stops.
Empowering Operators
In Autonomous Maintenance, operators take charge of basic maintenance tasks (cleaning, inspecting, and lubricating their equipment). This approach goes beyond mere tidiness; it cultivates a deep understanding of equipment functionality. Operators become the first line of defense against breakdowns, able to identify potential issues before they escalate into costly problems.
Breaking Down Departmental Silos
Traditional maintenance approaches often create divisions between operators and maintenance teams. Autonomous Maintenance eliminates these barriers. It promotes collaboration and knowledge sharing across departments, which leads to quicker problem-solving and more efficient operations overall.
Focus on Continuous Improvement
A key principle of Autonomous Maintenance is the pursuit of ongoing enhancement. It extends beyond maintaining the status quo; it involves a constant search for ways to improve equipment performance and reliability. This aligns perfectly with TPM’s goal to eliminate losses and maximize productivity.
Digital Tools for Implementation
Digital platforms support Autonomous Maintenance by providing tools for digital checklists, real-time issue reporting, and data analysis. These features help teams implement and sustain Autonomous Maintenance practices effectively. Weever Apps, for instance, offers a comprehensive solution that includes these essential features and more.
Implementing Autonomous Maintenance presents challenges. It requires a cultural shift and investment in training. However, the long-term benefits – increased uptime, reduced maintenance costs, and a more skilled workforce – make it a valuable strategy for many organizations. As we explore these benefits in more detail, you’ll see why more companies are adopting this approach.
Why Autonomous Maintenance Delivers Tangible Results
Slashing Downtime and Boosting Reliability
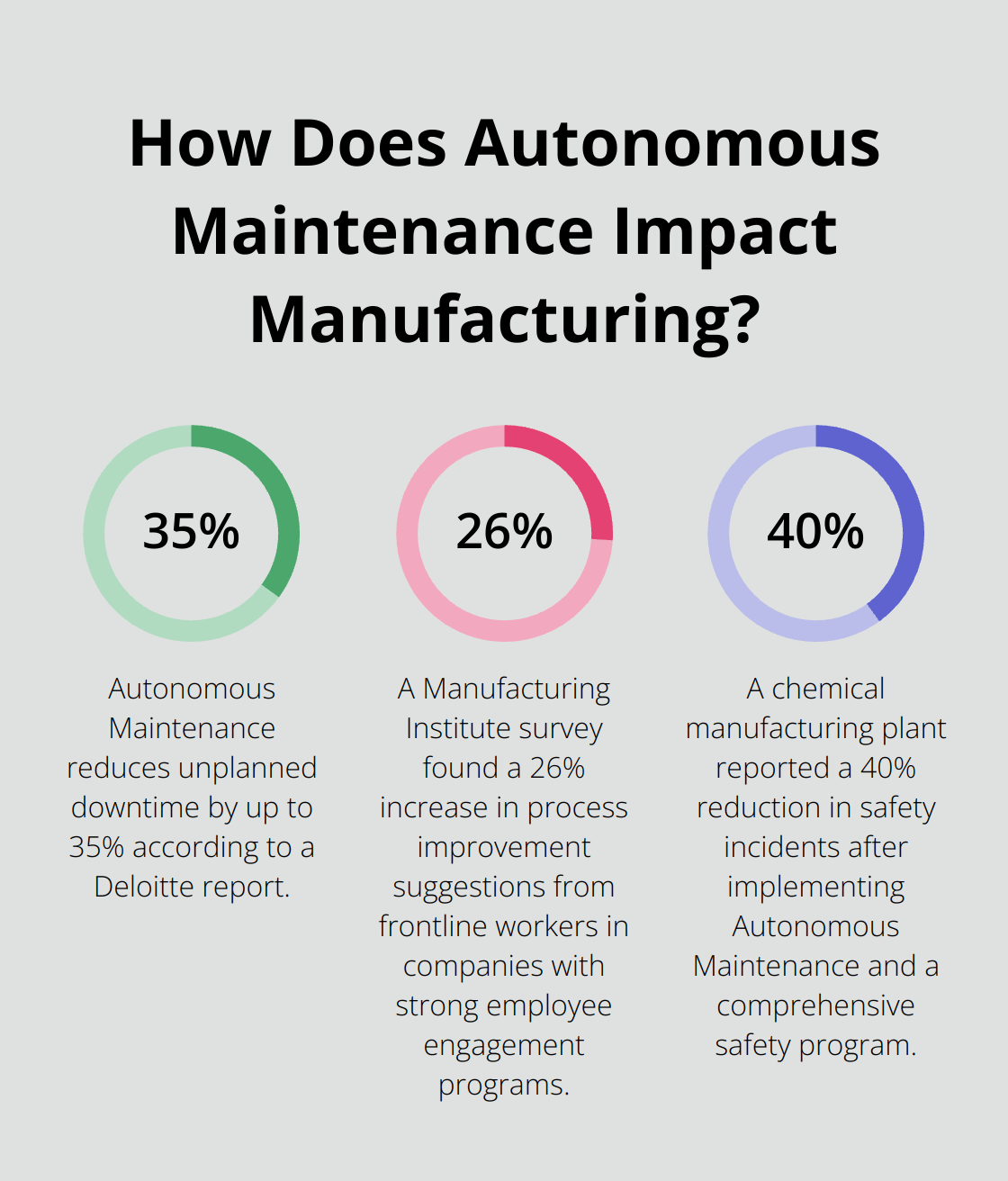
Unplanned downtime can cost a company up to $260,000 an hour. Autonomous Maintenance addresses this issue head-on. Operators who perform regular checks and minor repairs catch issues early. This proactive approach reduces unplanned downtime by up to 35% (according to a Deloitte report).
An automotive parts manufacturer in Michigan increased their Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) by 22% within six months of implementing Autonomous Maintenance. They achieved this result by empowering operators to conduct daily equipment checks and address minor issues immediately.
Cutting Maintenance Costs Without Compromising Quality
Maintenance budgets often spiral out of control, especially when companies rely heavily on reactive maintenance. Autonomous Maintenance reverses this trend. Companies expand their maintenance team without expanding their payroll when they involve operators in routine maintenance tasks.
A food processing plant in California reduced maintenance costs by 28% after implementing Autonomous Maintenance. They accomplished this by decreasing the frequency of major repairs and extending equipment life through better day-to-day care.
Elevating Product Quality Through Operator Expertise
Operators who know their equipment intimately spot quality issues before they escalate. This familiarity translates directly into improved product quality.
A textile manufacturer in North Carolina saw defect rates drop by 18% within the first year of implementing Autonomous Maintenance. Operators, now more attuned to their machines’ performance, quickly identified and corrected issues that previously led to quality problems.
Fostering a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Autonomous Maintenance extends beyond maintaining equipment; it continuously improves processes. Operators who take ownership of their equipment suggest improvements and innovations more frequently.
A Manufacturing Institute survey found that companies with strong employee engagement programs (like Autonomous Maintenance) saw a 26% increase in suggestions for process improvements from frontline workers.
Many companies turn to digital tools to support this culture of continuous improvement. These platforms allow operators to easily log observations, suggest improvements, and track the implementation of their ideas. This digital approach ensures that good ideas don’t fall through the cracks.
Enhancing Safety and Compliance
Autonomous Maintenance significantly improves workplace safety. Operators who regularly inspect and maintain their equipment identify potential hazards early, preventing accidents before they occur. This proactive approach not only protects workers but also ensures compliance with safety regulations.
A chemical manufacturing plant reported a 40% reduction in safety incidents after implementing Autonomous Maintenance (coupled with a comprehensive safety program). Regular equipment checks and immediate addressing of minor issues prevented many potential accidents.
As we explore the implementation of Autonomous Maintenance, we’ll discover how organizations can overcome common challenges and fully realize these benefits.
How to Implement Autonomous Maintenance
Create a Solid Foundation
Start with an assessment of your current maintenance practices. Identify equipment that will benefit most from Autonomous Maintenance. A food processing plant implemented Autonomous Maintenance and achieved time savings due to automated reporting through Weever’s integration with Microsoft Power BI.
Establish clear goals. Set specific, measurable targets for reducing downtime, cutting maintenance costs, or improving product quality. An automotive parts manufacturer in Michigan aimed to increase their Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) by 20% within six months.
Train and Empower Your Team
Effective training forms the cornerstone of successful implementation. Start with basic equipment knowledge and progress to more complex maintenance tasks. A chemical plant in Texas developed a tiered training program, which increased operator confidence in performing maintenance tasks by 30%.
Combine classroom sessions with hands-on practice. Digital learning platforms can enhance traditional training methods. For instance, some platforms offer interactive digital work instructions to guide operators through maintenance procedures step-by-step.
Cultural change plays an equally important role. Promote a sense of ownership among operators. Recognize and reward those who excel in their new responsibilities. A packaging company in Florida implemented a recognition program tied to Autonomous Maintenance achievements, resulting in a 25% increase in employee engagement scores.
Leverage Technology for Success
Digital tools streamline processes, improve communication, and provide valuable data insights for modern Autonomous Maintenance programs.
Mobile apps enable operators to log maintenance activities and report issues in real-time. A textile manufacturer in North Carolina implemented a mobile reporting system and reduced their response time to equipment issues by 40%.
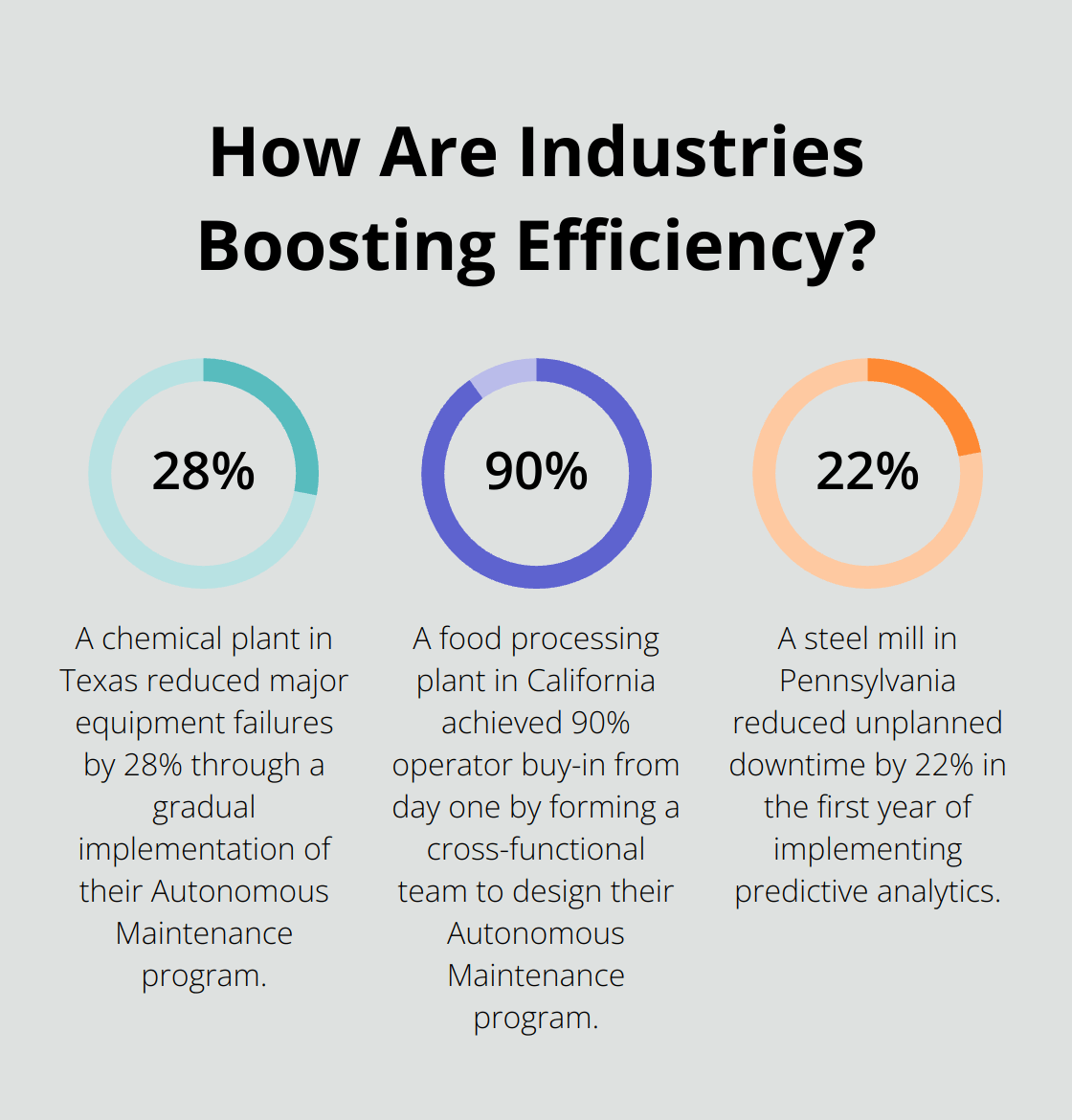
Data analytics platforms help identify trends and predict potential failures. A steel mill in Pennsylvania used predictive analytics to reduce unplanned downtime by 22% in the first year of implementation.
Choose a platform that integrates multiple functions. Some solutions combine digital checklists, real-time reporting, and data analytics in one user-friendly interface.
Overcome Common Challenges
Resistance to change often presents an obstacle. Address this by involving operators in the planning process and clearly communicating the benefits of Autonomous Maintenance. A food processing plant in California formed a cross-functional team to design their program, resulting in 90% operator buy-in from day one.
Consistency can pose another challenge. Implement standardized procedures and regular audits to ensure correct and consistent performance of maintenance tasks. An automotive parts manufacturer used digital checklists to increase compliance with maintenance procedures by 35%.
Try not to overwhelm your team. Start small and gradually expand your Autonomous Maintenance program. A chemical plant in Texas began with basic cleaning and inspection tasks, adding more complex maintenance activities over a six-month period. This approach led to a smooth transition and a 28% reduction in major equipment failures.
Final Thoughts
Autonomous maintenance transforms modern manufacturing with numerous benefits. Organizations reduce downtime, cut maintenance costs, and improve product quality when operators take ownership of their machinery. These improvements lead to enhanced safety, increased employee engagement, and a culture of continuous improvement.

The long-term impact of autonomous maintenance on organizational performance proves substantial. Companies that implement this strategy often see significant increases in Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), which translates directly to improved competitiveness. However, success requires unwavering commitment and a focus on continuous improvement.
Digital platforms play a crucial role in maximizing autonomous maintenance benefits. Weever’s Connected Worker platform offers a comprehensive solution for implementing and managing autonomous maintenance programs. With features like automated workflows and real-time dashboards, Weever helps organizations streamline their maintenance processes and drive continuous improvement.