Real-World Examples of Autonomous Maintenance in Action
Autonomous maintenance has revolutionized industries across the globe, boosting efficiency and reducing downtime. At Weever Apps, we’ve seen firsthand how this approach transforms operations in various sectors.
In this post, we’ll explore real-world autonomous maintenance examples from manufacturing, energy, and transportation. These case studies showcase the tangible benefits and future potential of this game-changing strategy.
How Do Manufacturing Giants Implement Autonomous Maintenance?
Toyota’s Pioneering Approach
Toyota has set the standard for autonomous maintenance implementation in manufacturing. The company’s focus on operator-led equipment care has yielded impressive results. PM targets are zero equipment failure and break down, improve reliability and maintainability by 50 percent, and reduce maintenance cost by 20 percent.
At the core of Toyota’s strategy lies their “5S” program (Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain). This systematic approach forms the foundation of their autonomous maintenance efforts. Operators maintain a clean, organized workspace, which allows them to spot and address potential issues early.
Siemens’ Digital Transformation
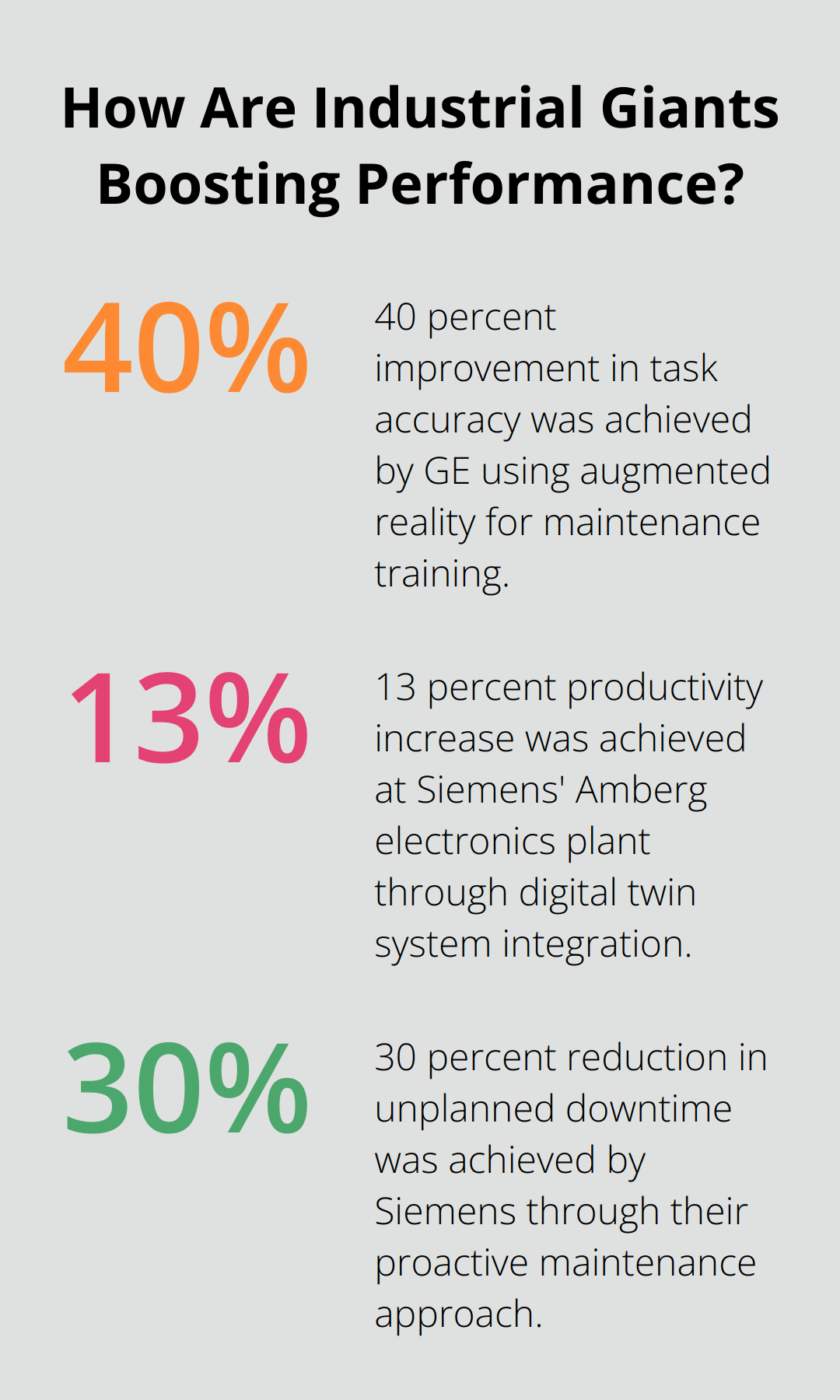
Siemens has integrated autonomous maintenance with Industry 4.0 technologies, taking the concept to new heights. Their Amberg electronics plant in Germany showcases this integration through a digital twin system. Operators monitor equipment performance in real-time, leading to a 13% productivity increase and a 99.9% quality rate (as reported by Siemens).
The company’s success stems from its use of data analytics to predict maintenance needs. Operators use tablets for instant access to equipment data, enabling informed decisions about maintenance tasks. This proactive approach has cut unplanned downtime by 30% and boosted overall equipment effectiveness by 20%.
General Electric’s Safety-First Approach
General Electric (GE) has leveraged autonomous maintenance to enhance worker safety and productivity. Their power generation facilities use a program called “Brilliant Factory,” which combines autonomous maintenance with advanced analytics.
GE Reports states that this initiative has reduced safety incidents related to equipment maintenance by 70%. The program empowers operators to perform routine checks and minor repairs, minimizing the need for specialized technicians in potentially hazardous areas.
GE also uses augmented reality (AR) for maintenance training. Operators use AR headsets for step-by-step guidance during maintenance procedures. This approach has cut training time by 60% and improved task accuracy by 40%.
Implementing Autonomous Maintenance in Your Organization
While these manufacturing giants have made significant strides, companies of all sizes can benefit from similar strategies. Platforms like Weever Apps offer comprehensive autonomous maintenance support, making it easier for businesses to implement these best practices and achieve comparable results.
As we move from manufacturing to the energy sector, we’ll see how companies like Vestas Wind Systems, Exelon, and Shell have adapted autonomous maintenance principles to their unique operational challenges.
How the Energy Sector Revolutionizes Maintenance
The energy sector faces unique challenges in maintaining complex, often remote infrastructure. Companies in this industry leverage autonomous maintenance to enhance efficiency, safety, and reliability. Industry leaders implement these strategies with impressive results.
Wind Power: Vestas Wind Systems’ Predictive Approach
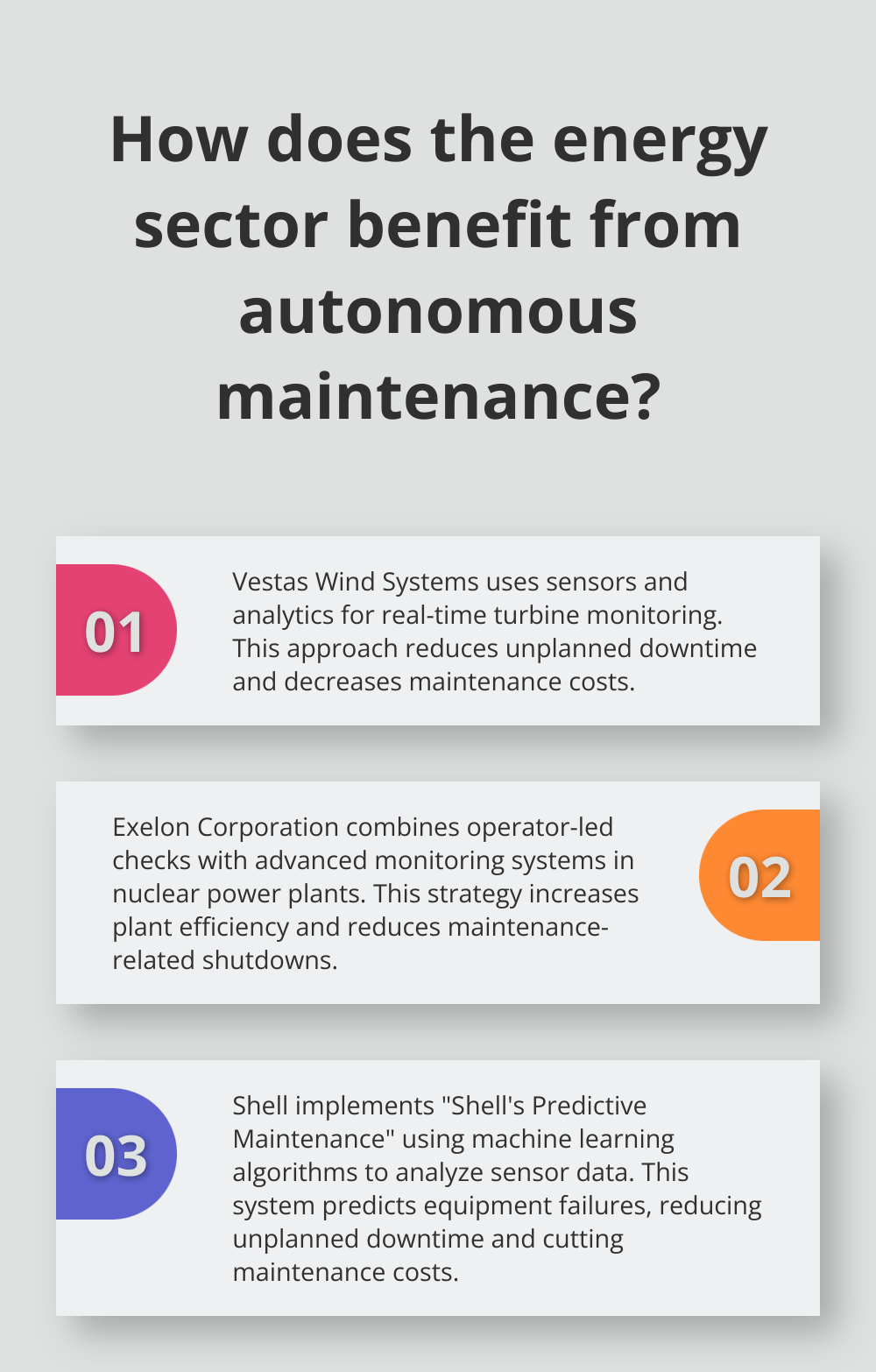
Vestas Wind Systems, a global leader in wind energy, embraces predictive maintenance for their wind turbines. The company uses a network of sensors and advanced analytics to monitor turbine performance in real-time. This approach has reduced unplanned downtime and decreased maintenance costs.
Vestas empowers technicians with mobile devices. These devices provide real-time data and step-by-step maintenance instructions, allowing for quick issue resolution. This has reduced the average repair time and improved technician safety by minimizing dangerous climbs.
Nuclear Power: Exelon’s Efficiency Drive
In the nuclear power sector, Exelon Corporation implements autonomous maintenance to enhance plant efficiency and safety. Their approach combines operator-led routine checks with advanced monitoring systems. This strategy has increased overall plant efficiency and reduced maintenance-related shutdowns.
Exelon’s success stems from their focus on operator training and engagement. They’ve developed a comprehensive program that teaches operators to perform basic maintenance tasks and identify potential issues early. This proactive approach has not only improved plant performance but also enhanced safety.
Oil and Gas: Shell’s Digital Transformation
Shell embraces digital transformation in its autonomous maintenance efforts. The company has implemented a system called “Shell’s Predictive Maintenance” across its global operations. This system uses machine learning algorithms to analyze data from thousands of sensors, predicting equipment failures before they occur.
This approach has reduced unplanned downtime and cut maintenance costs. The system also enhances worker safety by minimizing the need for routine inspections in hazardous areas.
A key component of Shell’s strategy is the use of digital twins (virtual replicas of physical assets). These allow operators to simulate different scenarios and optimize maintenance schedules without risking actual equipment. This has led to improvements in equipment lifespan and reductions in energy consumption.
While these energy giants have made significant strides with custom solutions, smaller companies can achieve similar results using platforms like Weever Apps. Weever’s Connected Worker platform offers many of the same benefits, including real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance capabilities, and enhanced worker safety, all in a more accessible package.
The transportation sector also applies autonomous maintenance principles to keep vehicles and infrastructure in top condition. Let’s explore how companies in this industry implement these strategies to improve efficiency and safety.
How Transportation Revolutionizes Maintenance
The transportation sector faces unique challenges in maintaining complex vehicles and infrastructure. Airlines, railways, and automotive companies now leverage autonomous maintenance to enhance safety, efficiency, and reliability. Industry leaders implement these strategies with impressive results.
Delta’s High-Flying Maintenance Program
Delta Air Lines has implemented a predictive analytics and maintenance program for its engines and airframes. The airline uses a system that analyzes data from sensors on each plane. This approach aims to reduce maintenance-related issues and improve efficiency.
Delta’s technicians use advanced technology for maintenance tasks. These devices assist technicians through complex procedures, potentially improving repair times and fix rates.
Network Rail’s Track to Efficiency
Network Rail, responsible for Britain’s railway infrastructure, has embraced autonomous maintenance to keep its vast network running smoothly. The company uses autonomous inspection trains equipped with high-resolution cameras and laser scanners to monitor track conditions. These trains can cover up to 1,000 miles per day, significantly more than manual inspections.
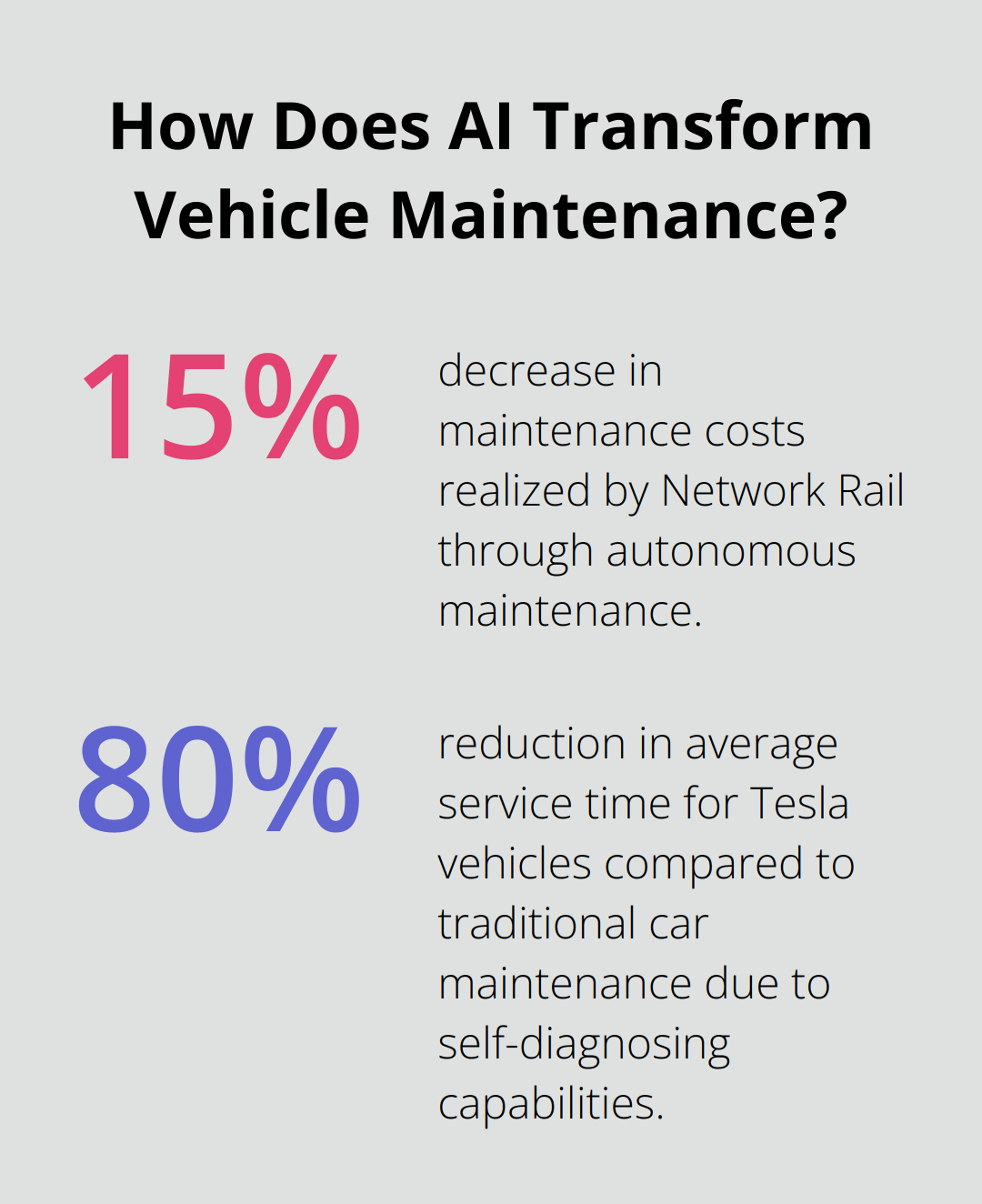
This approach has led to a 30% reduction in track-related delays and a 15% decrease in maintenance costs. Network Rail’s success stems from its focus on data integration. The company uses a centralized system that combines inspection data with maintenance schedules, allowing for more efficient resource allocation.
Tesla’s Self-Diagnosing Vehicles
Tesla has taken autonomous maintenance to the consumer level with its self-diagnosing vehicles. Each Tesla car is equipped with sensors that continuously monitor vehicle health. When an issue is detected, the car can often perform minor software updates automatically or alert the driver to schedule a service appointment.
This proactive approach has reduced the average service time for Tesla vehicles by 80% compared to traditional car maintenance. It has also improved customer satisfaction, with Tesla consistently ranking high in J.D. Power’s Vehicle Dependability Study.
Implementing Autonomous Maintenance in Transportation
While these transportation giants have made significant strides with custom solutions, smaller companies can achieve similar results using platforms like Weever Apps. Weever’s Connected Worker platform offers many of the same benefits (including real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance capabilities, and enhanced worker safety), all in a more accessible package.
As we’ve seen, autonomous maintenance transforms operations across various industries. From manufacturing to energy and now transportation, companies reap the benefits of this innovative approach.
Final Thoughts
The autonomous maintenance examples we explored highlight the transformative power of this approach across industries. Companies implementing these strategies report significant cost savings, increased productivity, and better overall equipment effectiveness. The integration of advanced technologies like AI, IoT sensors, and augmented reality has further amplified these benefits, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time decision-making.

Autonomous maintenance is not just a trend; it has become a necessity for companies aiming to stay competitive in an increasingly digital world. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated applications. The increasing accessibility of these technologies means that businesses of all sizes can now implement autonomous maintenance strategies.
Weever Apps makes it easier than ever for companies to adopt these practices, offering comprehensive solutions that support autonomous maintenance programs. These tools enhance worker engagement and drive operational efficiency (without compromising safety). Companies that successfully integrate autonomous maintenance into their core operations will thrive, continuously adapting and improving their approaches to meet evolving industry demands.