The Autonomous Maintenance Pillar: Foundation for Success
At Weever Apps, we’ve seen firsthand how the autonomous maintenance pillar can transform manufacturing operations.
This approach empowers operators to take ownership of equipment care, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime.
In this post, we’ll explore the core principles of autonomous maintenance, provide a step-by-step implementation guide, and address common challenges.
Get ready to revolutionize your maintenance strategy and boost your operational excellence.
What is Autonomous Maintenance?
Redefining Equipment Care
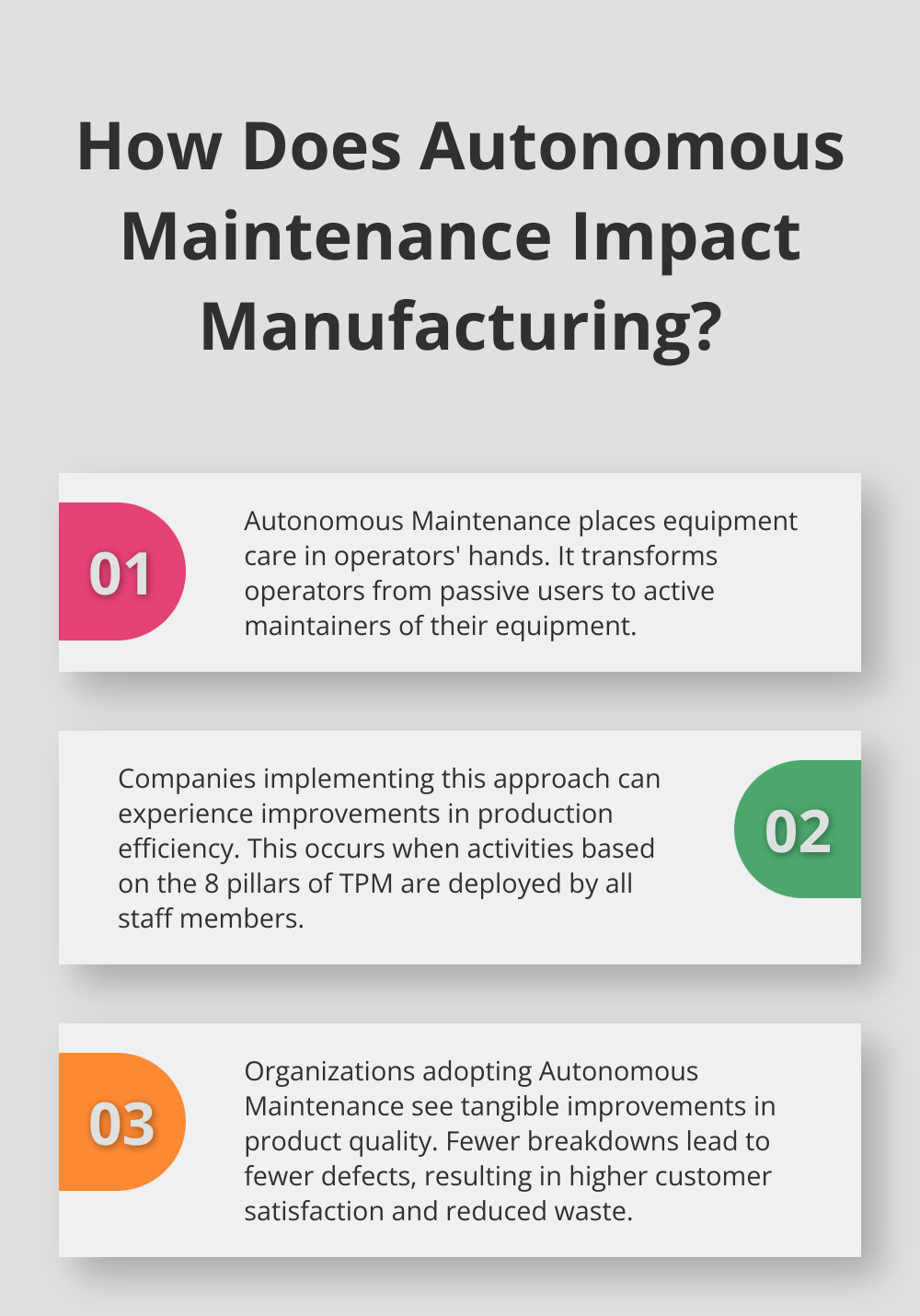
Autonomous Maintenance revolutionizes equipment care by placing it directly in the hands of operators. This strategy transforms the workforce from mere machine operators into active maintainers of their equipment.
The Operator’s Expanded Role
Traditional maintenance models often relegate operators to a passive role in equipment upkeep. They run machines but call in the maintenance team when issues arise. Autonomous Maintenance completely reverses this approach.
Operators now serve as the primary defense against equipment failures. They receive training to perform basic maintenance tasks, identify early signs of wear, and execute minor repairs. This responsibility shift creates a more engaged and knowledgeable workforce.
Quantifiable Benefits for Manufacturing
The impact of Autonomous Maintenance on manufacturing and production yields significant, measurable results. Companies implementing this approach can experience improvements in production efficiency when they have deployed activities based on the 8 pillars of TPM by all staff members of the plants/factories, including individual improvement, autonomous maintenance, and planned maintenance.
Furthermore, organizations adopting Autonomous Maintenance principles see tangible improvements in product quality. Fewer breakdowns translate to fewer defects, leading to higher customer satisfaction and reduced waste.
A Paradigm Shift in Maintenance Strategy
Autonomous Maintenance represents a fundamental change in equipment care philosophy. It moves away from reactive maintenance (fixing things after they break) towards a proactive model where potential issues receive identification and resolution before causing downtime.
This approach aligns perfectly with lean manufacturing principles, focusing on waste reduction and process efficiency. Empowering operators to take ownership of their equipment fosters a culture of continuous improvement that extends far beyond the maintenance department.
Technology’s Role in Autonomous Maintenance
Modern Connected Worker platforms support and enhance Autonomous Maintenance initiatives. Digital tools simplify the logging of maintenance activities, provide easy access to equipment manuals, and enable real-time communication of issues. This seamless integration of technology and maintenance strategy (a key feature of platforms like Weever) maximizes the benefits of Autonomous Maintenance in today’s digital-first manufacturing environment.
As we move forward, we’ll explore the step-by-step process of implementing Autonomous Maintenance in your organization, ensuring you can harness its full potential.
How to Implement Autonomous Maintenance
Assess Your Current State
Start by evaluating your existing maintenance practices. Identify equipment that frequently breaks down or causes production delays. This assessment will help you prioritize which areas to focus on first. Use data from your maintenance management system to pinpoint recurring issues and their root causes.
Develop a Pilot Program
Initiate a small-scale pilot program on a single production line or piece of equipment. This approach allows you to refine your implementation strategy before a company-wide rollout. Select a team that’s open to change and eager to learn new skills.
Train Your Operators
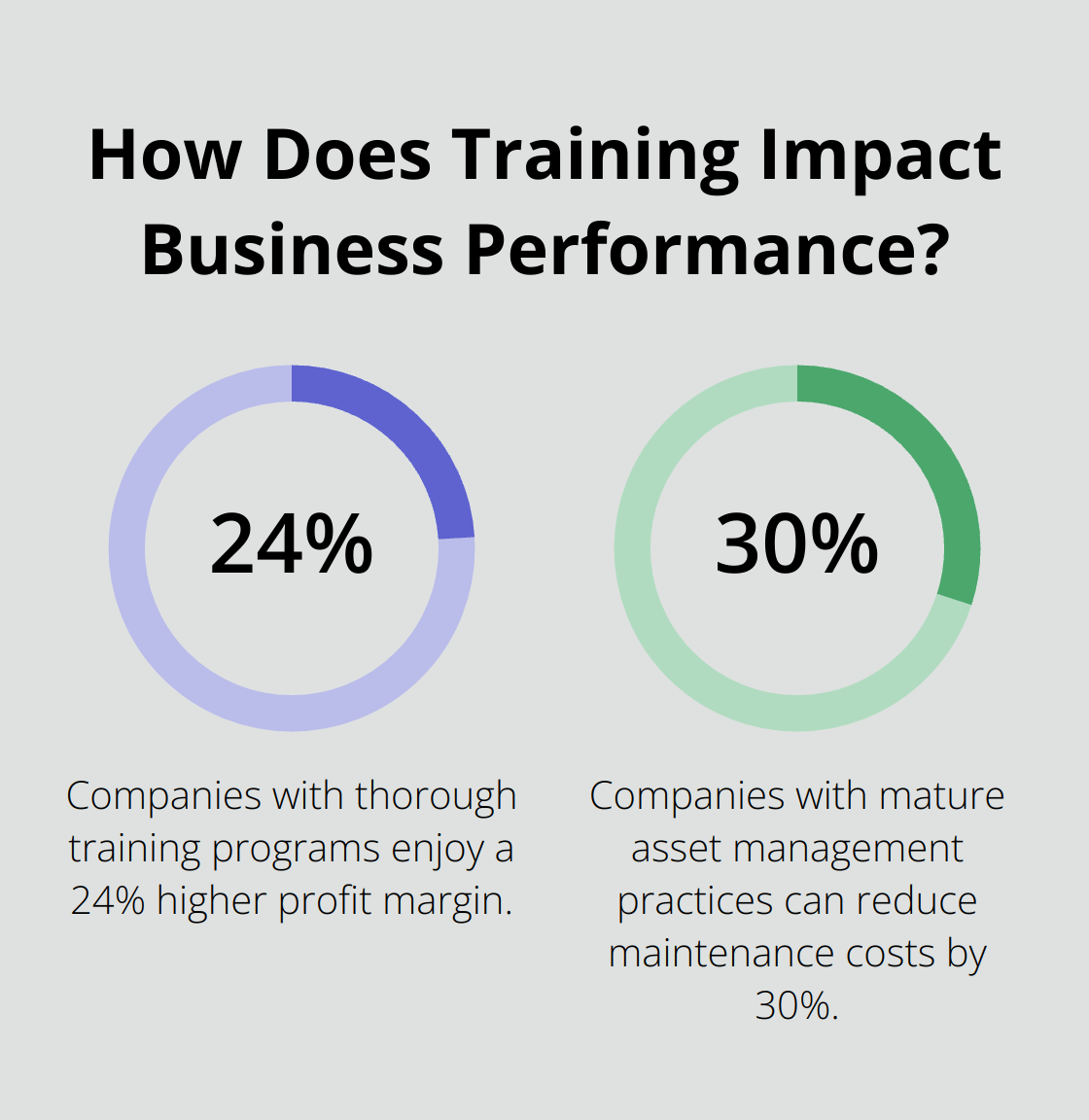
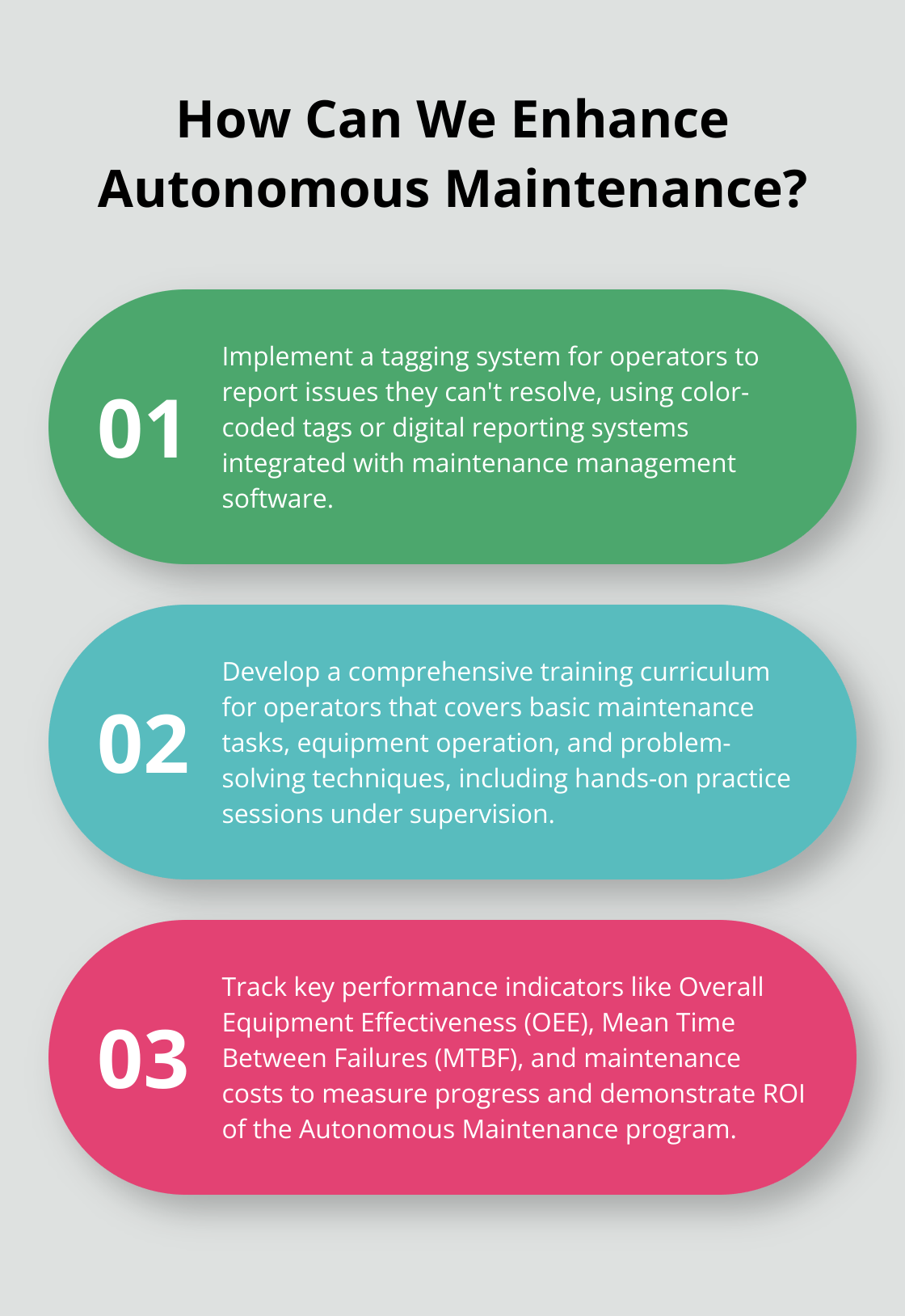
Comprehensive training is essential for success. Develop a curriculum that covers basic maintenance tasks, equipment operation, and problem-solving techniques. Include hands-on practice sessions where operators can apply their new skills under supervision. Companies with thorough training programs have 218% higher income per employee and enjoy a 24% higher profit margin.
Create Standard Operating Procedures
Develop clear, step-by-step procedures for each maintenance task. Make these easily accessible and understandable. Digital platforms can prove invaluable here, allowing you to create interactive, multimedia SOPs that operators can access on mobile devices right at their workstations.
Implement a Tagging System
Introduce a system for operators to tag and report issues they can’t resolve themselves. This could range from simple color-coded tags to sophisticated digital reporting systems integrated with your maintenance management software. Establish a clear process for addressing these tags and designate responsible personnel.
Monitor and Measure Progress
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), and maintenance costs. Regular reviews of these metrics will help you identify areas for improvement and demonstrate the ROI of your Autonomous Maintenance program. The Society for Maintenance and Reliability Professionals reports that companies with mature asset management practices can reduce maintenance costs by 25-30%.
Implementing Autonomous Maintenance is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement and adaptation. The next section will address common challenges you might face during this implementation and provide strategies to overcome them.
Navigating Roadblocks in Autonomous Maintenance
Addressing Employee Resistance
One of the most significant hurdles in implementing Autonomous Maintenance (AM) is employee resistance. Workers may feel threatened by the changes or doubt their ability to take on new responsibilities. To combat this, focus on clear communication and comprehensive training.

Explain the benefits of AM not just for the company, but for the employees themselves. Highlight how their roles will become more skilled and valuable. By upskilling through AM, employees become more marketable and secure in their positions.
Involve employees in the planning process. This gives them a sense of ownership and helps address their concerns early on. Create a mentorship program where experienced maintenance staff guide operators through the transition. This builds confidence and fosters a collaborative environment.
Seamless Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating AM with existing maintenance systems can be complex. The key is to start small and scale gradually. Begin by identifying areas where AM can complement your current processes rather than replace them entirely.
Utilize digital platforms that can bridge the gap between your existing systems and new AM processes. For instance, Connected Worker platforms can integrate with your current CMMS, allowing for a smooth transition to AM while maintaining data continuity.
Conduct regular audits of your maintenance processes to identify redundancies and inefficiencies. This helps streamline the integration of AM and ensures that your overall maintenance strategy remains cohesive.
Quantifying Success and ROI
Measuring the impact of AM can be challenging, but it’s essential for demonstrating its value to stakeholders. Establish clear KPIs before implementation. These might include Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), and maintenance costs.
Use digital tools to track these metrics in real-time. Many companies struggle with accurate data collection, but modern platforms can automate this process, ensuring you have reliable data to work with.
Don’t just focus on hard metrics. Soft benefits like improved employee engagement and reduced stress on the maintenance team are also valuable. Survey your workforce regularly to capture these qualitative improvements.
The full benefits of AM may take time to materialize. Be patient and focus on continuous improvement. Regular reviews and adjustments to your AM strategy will help maximize its impact over time.
Final Thoughts
The autonomous maintenance pillar transforms manufacturing operations. It empowers operators to care for equipment, reduces downtime, and cuts maintenance costs. This approach fosters a culture of continuous improvement and increases employee engagement throughout the organization.
Companies that adopt autonomous maintenance position themselves for long-term success. They create a more resilient and adaptive production environment, ready to face evolving industrial challenges. The journey starts with a clear assessment of current practices and a commitment to change, followed by focused pilot programs and comprehensive training.
We at Weever Apps have seen the power of autonomous maintenance supported by the right digital tools. Our Connected Worker platform enhances implementation with intuitive digital forms, real-time dashboards, and automated workflows. These features drive engagement and ensure easy access to critical information, setting the foundation for operational excellence in the global marketplace.