Autonomous Maintenance: SlideShare Insights
Autonomous maintenance is revolutionizing how industries approach equipment upkeep. This innovative strategy empowers operators to take charge of routine maintenance tasks, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime.
At Weever Apps, we’ve seen firsthand the transformative impact of autonomous maintenance on manufacturing processes. Our SlideShare presentation offers valuable insights into this game-changing approach, showcasing real-world examples and practical implementation strategies.
What is Autonomous Maintenance?
The Core of Autonomous Maintenance
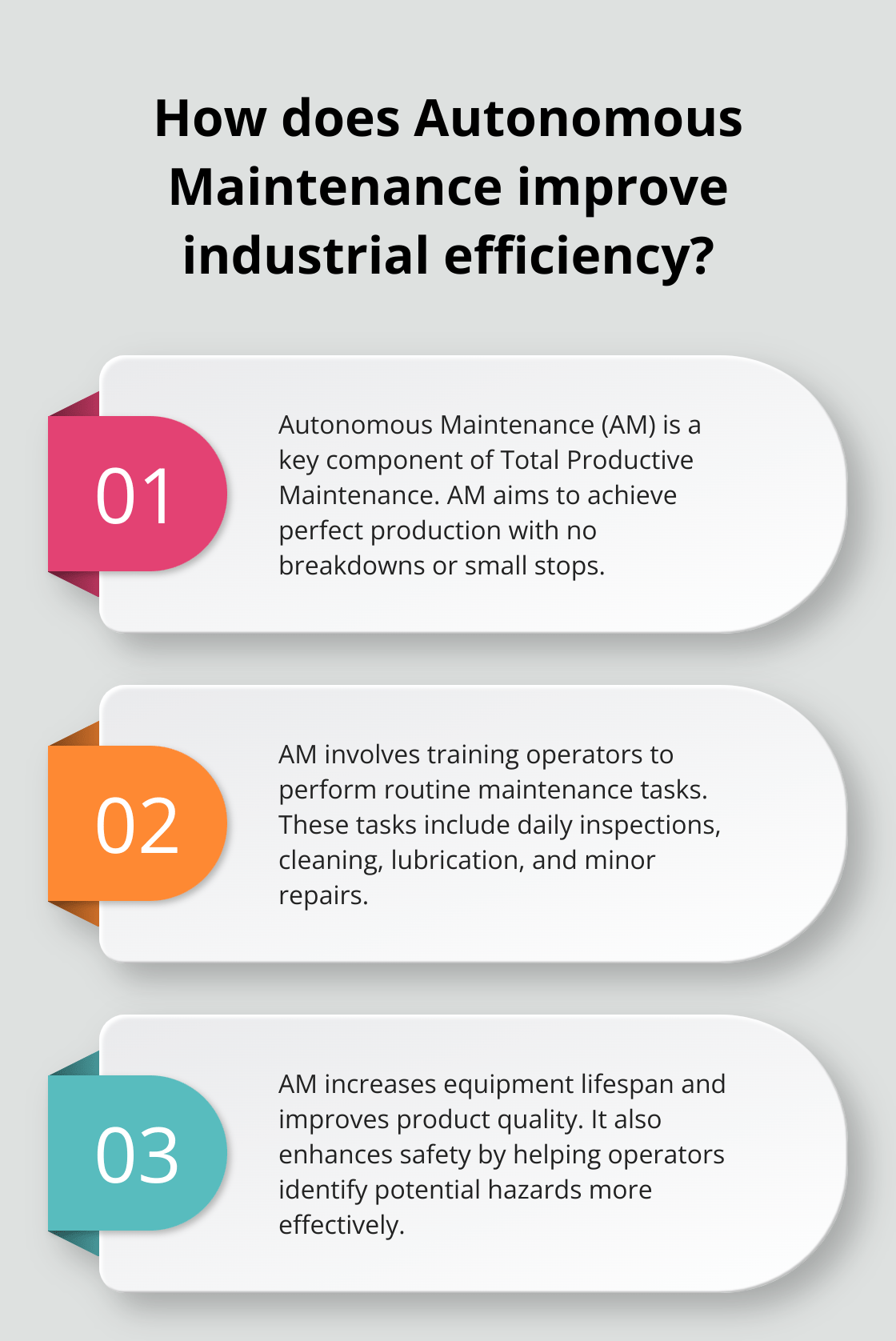
Autonomous Maintenance (AM) is a proactive approach that puts equipment care directly in the hands of operators. It forms a key component of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) and aims to achieve perfect production with no breakdowns or small stops.
AM involves training operators to perform routine maintenance tasks traditionally handled by specialized maintenance teams. These tasks include daily inspections, cleaning, lubrication, and minor repairs. This empowerment allows companies to address small issues before they escalate into major problems.
Transforming Industrial Efficiency
The benefits of AM extend far beyond reducing downtime. In manufacturing and industrial settings, AM leads to:
- Increased equipment lifespan: Regular care by operators who intimately know their machines can extend equipment life.
- Improved product quality: When operators maintain their equipment, they spot and correct issues that could affect product quality more easily.
- Enhanced safety: Operators who engage more with their equipment identify potential safety hazards more effectively.
Breaking from Traditional Maintenance
AM marks a significant shift from traditional maintenance approaches. Here’s how it differs:
- Proactive vs. Reactive: Traditional maintenance often waits for breakdowns to occur. AM focuses on preventing issues before they happen.
- Operator Empowerment: Unlike traditional models where operators simply run machines, AM trains them to be the first line of defense against equipment issues.
- Continuous Improvement: AM encourages operators to suggest improvements based on their daily interactions with the equipment.
Implementing Autonomous Maintenance
Implementing AM requires a cultural shift and investment in training, but the returns can be substantial. Companies that fully embrace AM often see improvements in Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), which can translate to cost savings and competitive advantages in their industries.
To successfully implement AM, companies need to follow a structured approach. This includes creating a clear roadmap, providing comprehensive training, and utilizing the right tools and technologies. In the next section, we’ll explore the steps and resources necessary for a successful AM implementation.
How to Implement Autonomous Maintenance
Steps for Successful Implementation
Autonomous Maintenance (AM) implementation starts with a thorough assessment of current maintenance practices. This initial step identifies areas for improvement and sets the stage for change. Organizations must then establish clear goals and metrics for their AM program, such as targets for reducing equipment downtime or improving Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE).
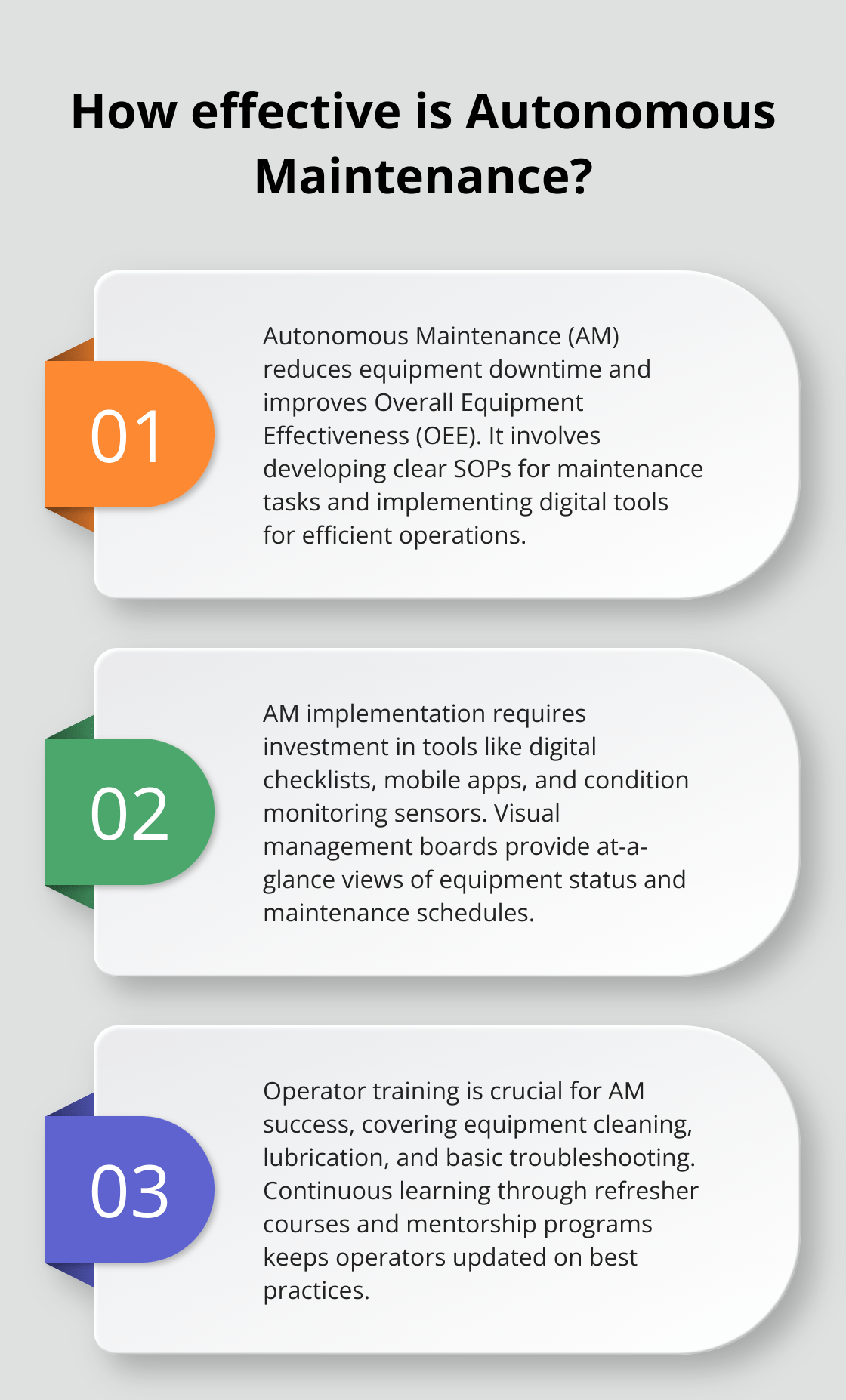
A critical phase in AM implementation involves the development of standard operating procedures (SOPs) for maintenance tasks. These SOPs should be clear, concise, and easily accessible to operators.
Essential Tools for Autonomous Maintenance
Companies need to invest in the right tools and technologies to support AM initiatives. Digital checklists and mobile apps have become indispensable for modern AM programs. These tools allow operators to easily record inspections, report issues, and access maintenance information on the go.
Condition monitoring sensors are another vital component of effective AM. These devices can detect early signs of equipment wear or malfunction, enabling proactive maintenance.
Visual management boards provide a clear, at-a-glance view of equipment status, maintenance schedules, and performance metrics. They help foster transparency and accountability among team members.
Training: The Cornerstone of Autonomous Maintenance
Autonomous maintenance increases efficiency by training operators to perform minor maintenance tasks. This training should cover topics such as equipment cleaning, lubrication, and basic troubleshooting.
Continuous learning plays a key role in AM success. Regular refresher courses and skill-building workshops help keep operators up-to-date with best practices and new technologies. Some companies have seen success with mentorship programs, where experienced operators guide newer team members in AM practices.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Implementing AM requires a shift in organizational culture and a commitment to ongoing improvement. Companies often face resistance to change and may struggle with initial resource allocation. However, clear communication about the benefits of AM (reduced downtime, improved equipment reliability, and increased operator engagement) can help overcome these hurdles.
To support the implementation of Autonomous Maintenance and other key operational initiatives, many organizations turn to digital solutions. Weever’s Connected Worker platform offers features specifically designed to enhance AM programs, including automated workflows, real-time dashboards, and intuitive digital forms for easy data capture. These tools can significantly streamline the transition to an AM-focused approach.
As organizations progress through their AM implementation journey, they often discover valuable insights and success stories. The next section will explore real-world examples of AM in action and the measurable improvements companies have achieved.
Real-World Wins with Autonomous Maintenance
Toyota’s Efficiency Boost
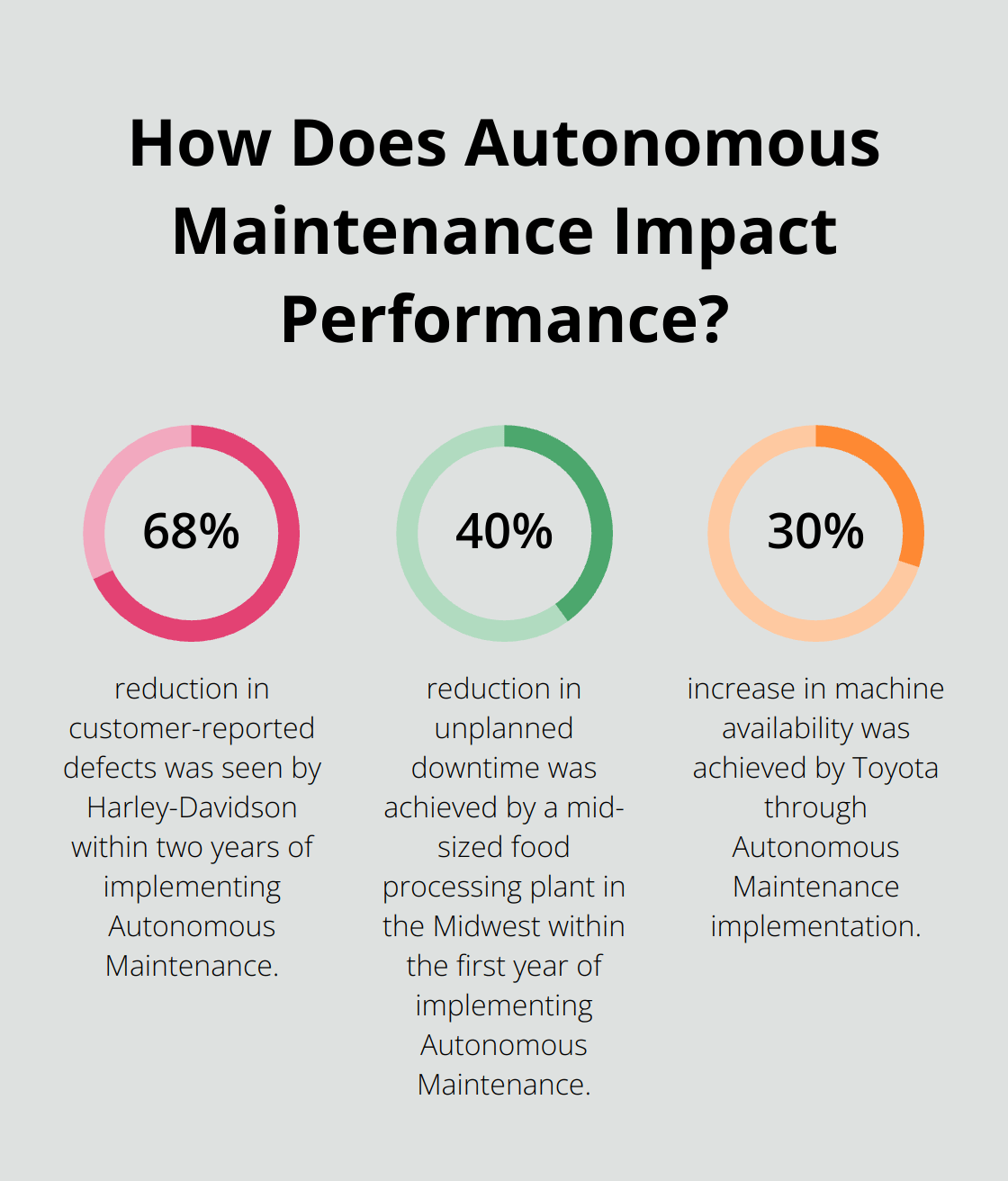
Toyota, a pioneer in lean manufacturing, implemented Autonomous Maintenance (AM) as part of its Toyota Production System. The company reported a 50% reduction in equipment breakdowns and a 30% increase in machine availability. This improvement led to an estimated annual savings of $3.5 million per plant.
Toyota’s success relied on thorough operator training and a cultural shift towards equipment ownership. The company invested heavily in visual management tools, creating clear, standardized procedures for daily maintenance tasks. This approach improved equipment reliability and boosted operator morale and engagement.
Harley-Davidson’s Quality Revolution
Harley-Davidson’s adoption of AM led to remarkable improvements in product quality and operational efficiency. The motorcycle manufacturer saw a 68% reduction in customer-reported defects and a 35% decrease in warranty costs within two years of implementation.
The key to Harley-Davidson’s success was its focus on operator empowerment. The company developed a comprehensive training program that taught operators not just how to maintain equipment, but why each task mattered. This deeper understanding led to more proactive problem-solving and continuous improvement suggestions from the shop floor.
Critical Success Factors
These success stories highlight several critical factors for effective AM implementation:
- Leadership commitment is essential. Both Toyota and Harley-Davidson ensured full support from top management, which proved vital for overcoming initial resistance and securing necessary resources.
- Training and education are paramount. Successful AM programs build a deep understanding of equipment and processes among operators (not just teaching tasks).
- Technology enhances effectiveness. While AM focuses on operator empowerment, the right digital tools can significantly improve its impact. Connected Worker platforms provide real-time data capture and analysis capabilities, streamlining AM processes for many organizations.
- Pilot programs pave the way. Many successful AM implementations start small before expanding company-wide. This approach allows for fine-tuning and building internal champions.
- Regular tracking matters. Consistent monitoring and sharing of key performance indicators (KPIs) help maintain momentum and justify further investment in AM initiatives.
Small and Medium Enterprise Success
The success of AM isn’t limited to large corporations. A mid-sized food processing plant in the Midwest implemented AM and saw a 40% reduction in unplanned downtime within the first year, translating to an estimated $500,000 in savings.
These real-world examples demonstrate that Autonomous Maintenance can deliver substantial improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost savings across various industries and company sizes.
Final Thoughts
Autonomous maintenance revolutionizes modern manufacturing and industrial settings. Companies empower operators to own routine maintenance tasks, which reduces downtime, extends equipment lifespan, and improves operational efficiency. Success stories prove that AM delivers tangible results across various industries and company sizes.

The future of maintenance strategies will integrate digital technologies further. Industrial Internet of Things sensors and artificial intelligence will enhance predictive maintenance capabilities, allowing for more proactive equipment care. Operators’ roles in autonomous maintenance will become more sophisticated, necessitating ongoing training and skill development.
Weever Apps supports organizations in their autonomous maintenance initiatives with our Connected Worker platform. Our platform offers tools to streamline AM implementation and maximize its benefits. Resources like Autonomous Maintenance SlideShare presentations will continue to play a vital role in sharing best practices and implementation strategies.